Exploring the Virtualization Landscape: Windows 11 in a Digital Sandbox
Related Articles: Exploring the Virtualization Landscape: Windows 11 in a Digital Sandbox
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Virtualization Landscape: Windows 11 in a Digital Sandbox. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Virtualization Landscape: Windows 11 in a Digital Sandbox
The world of computing has long embraced virtualization, a technology that allows users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical machine. This capability has revolutionized how individuals and organizations approach their computing needs, offering flexibility, efficiency, and a host of other advantages. Within this landscape, the ability to run Windows 11 within a virtual environment has emerged as a powerful tool, providing numerous benefits for diverse users.
Understanding Virtualization: The Foundation of Digital Flexibility
Virtualization works by creating a software-based emulation of a physical computer system. This "virtual machine" (VM) can run its own operating system, applications, and data, completely isolated from the host machine. This isolation provides a crucial layer of security, preventing potential conflicts and ensuring that the host system remains unaffected by actions within the VM.
Windows 11 Virtualization: A Gateway to New Possibilities
Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, has embraced virtualization with open arms. Its built-in features and compatibility with popular virtualization software make it an ideal platform for creating and managing virtual machines. This opens doors to a wide range of applications, catering to both personal and professional needs.
Benefits of Running Windows 11 in a Virtual Machine
The advantages of running Windows 11 within a virtual environment are multifaceted, offering solutions for various scenarios:
- Testing and Development: Virtual machines provide a safe and controlled environment for software development and testing. Developers can experiment with new code, install different software versions, and explore new configurations without affecting their primary operating system.
- Security and Isolation: Running a potentially risky application within a VM isolates it from the host system, protecting critical data and ensuring that any security breaches are confined to the virtual environment.
- Legacy Software Compatibility: Virtual machines can run older software that is no longer compatible with the latest operating systems, ensuring continued access to essential applications.
- Multiple Operating System Environments: Users can run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer, enabling seamless switching between different platforms and environments.
- Resource Management: Virtual machines allow users to allocate specific resources like CPU, RAM, and storage to individual VMs, optimizing performance and ensuring that each VM receives the resources it needs.
- Disaster Recovery: Virtual machines can be used to create backups and replicas of critical data and applications, enabling rapid recovery in case of hardware failure or other unforeseen events.
- Accessibility: Virtual machines can provide access to specialized software or tools that might not be available on the host system, opening up new possibilities for users with specific requirements.
Popular Virtualization Software for Windows 11
Several popular virtualization software options are available for creating and managing Windows 11 virtual machines. Some of the most widely used include:
- VMware Workstation: A powerful and feature-rich virtualization platform known for its performance and stability.
- Oracle VirtualBox: A free and open-source virtualization solution offering a user-friendly interface and broad compatibility.
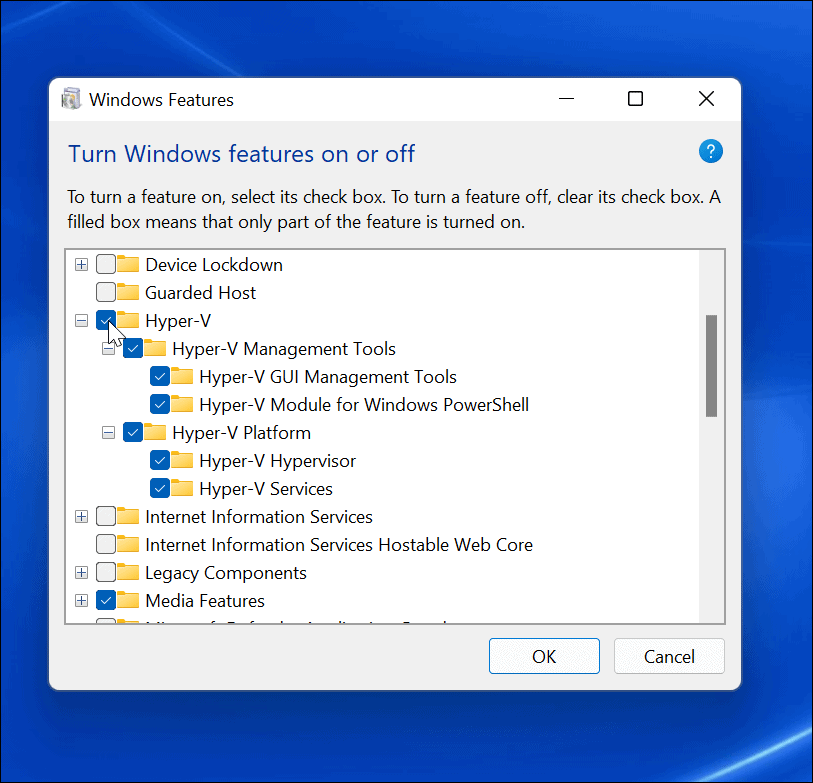
- Microsoft Hyper-V: A built-in virtualization platform for Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions, providing native integration and performance optimization.
- Parallels Desktop: A virtualization solution designed specifically for macOS users, offering seamless integration and easy management of Windows 11 virtual machines.
Choosing the Right Virtualization Software
The best virtualization software for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Factors to consider include:
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure the software supports your host and guest operating systems.
- Performance Requirements: Consider the performance demands of your virtual machines and choose software that can handle those requirements.
- Features and Functionality: Evaluate the features offered by each software, such as advanced networking, storage management, and security features.
- Cost: Compare the pricing models of different software options, ranging from free to paid subscriptions.
Setting Up a Windows 11 Virtual Machine: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a Windows 11 virtual machine is a straightforward process, typically involving these steps:
- Download and Install Virtualization Software: Choose your preferred virtualization software and download and install it on your host machine.
- Create a New Virtual Machine: Launch the virtualization software and create a new virtual machine. Specify the desired operating system (Windows 11) and allocate resources like CPU, RAM, and storage.
- Install Windows 11 in the Virtual Machine: Download a Windows 11 ISO file and use it to install the operating system within the virtual machine.
- Configure the Virtual Machine: Adjust settings like network configuration, shared folders, and display resolution to optimize the virtual machine’s performance and functionality.
- Install Drivers: Install necessary drivers for the virtual machine to access hardware resources like graphics, sound, and network.
- Optimize Performance: Fine-tune the virtual machine’s settings to ensure optimal performance based on your specific needs and hardware capabilities.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the system requirements for running Windows 11 in a virtual machine?
A: The system requirements for running Windows 11 in a virtual machine are similar to those for running it on a physical computer. However, you’ll need additional resources to accommodate the host operating system and the virtual machine. Generally, a modern processor with multiple cores, at least 8GB of RAM, and a dedicated hard drive space of at least 64GB are recommended.
Q: Can I run Windows 11 virtual machines on a Mac?
A: Yes, you can run Windows 11 virtual machines on a Mac using virtualization software like Parallels Desktop or VMware Fusion. These platforms offer seamless integration and provide a near-native experience for running Windows 11 on a macOS system.
Q: Is it legal to run Windows 11 in a virtual machine?
A: Legally, running Windows 11 in a virtual machine is generally acceptable. However, it’s crucial to ensure that you have a valid license for the Windows 11 operating system. If you’re using a trial version or an unlicensed copy, you might face legal repercussions.
Q: Can I use a Windows 11 virtual machine for gaming?
A: While you can technically run games within a Windows 11 virtual machine, it’s not recommended for optimal performance. Virtualization introduces a layer of overhead, which can lead to reduced frame rates and lag. For gaming, it’s generally preferable to run games directly on the host operating system.
Q: What are the limitations of running Windows 11 in a virtual machine?
A: While virtualization offers many advantages, it also comes with some limitations. Performance can be affected by the resources allocated to the virtual machine, and certain hardware features might not be fully supported. Additionally, some software applications might not run correctly within a virtual environment.
Tips for Optimizing Performance and Functionality
- Allocate Sufficient Resources: Ensure that the virtual machine is allocated enough CPU cores, RAM, and storage space to meet its performance requirements.
- Use a Dedicated Hard Drive: Create a dedicated hard drive for the virtual machine to improve performance and minimize potential conflicts with other applications.
- Enable Hardware Acceleration: Enable hardware acceleration within the virtualization software to leverage the host system’s resources and boost performance.
- Adjust Display Settings: Fine-tune the virtual machine’s display settings to ensure optimal resolution and responsiveness.
- Install Necessary Drivers: Install any necessary drivers for the virtual machine to access hardware features like graphics, sound, and network.
- Regularly Update Virtualization Software: Keep the virtualization software updated to benefit from performance improvements, bug fixes, and new features.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Virtualization
Running Windows 11 within a virtual machine offers a powerful and flexible approach to computing, providing a range of benefits for diverse users. From software development and testing to security enhancement and legacy software compatibility, virtualization empowers individuals and organizations to optimize their workflows, enhance productivity, and explore new possibilities. As the world of computing continues to evolve, virtualization will likely play an increasingly crucial role, shaping how we interact with technology and unlock the full potential of our digital environments.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Virtualization Landscape: Windows 11 in a Digital Sandbox. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
