Navigating the TPM Requirement: An Exploration of Windows 11 Compatibility and Workarounds
Related Articles: Navigating the TPM Requirement: An Exploration of Windows 11 Compatibility and Workarounds
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the TPM Requirement: An Exploration of Windows 11 Compatibility and Workarounds. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the TPM Requirement: An Exploration of Windows 11 Compatibility and Workarounds
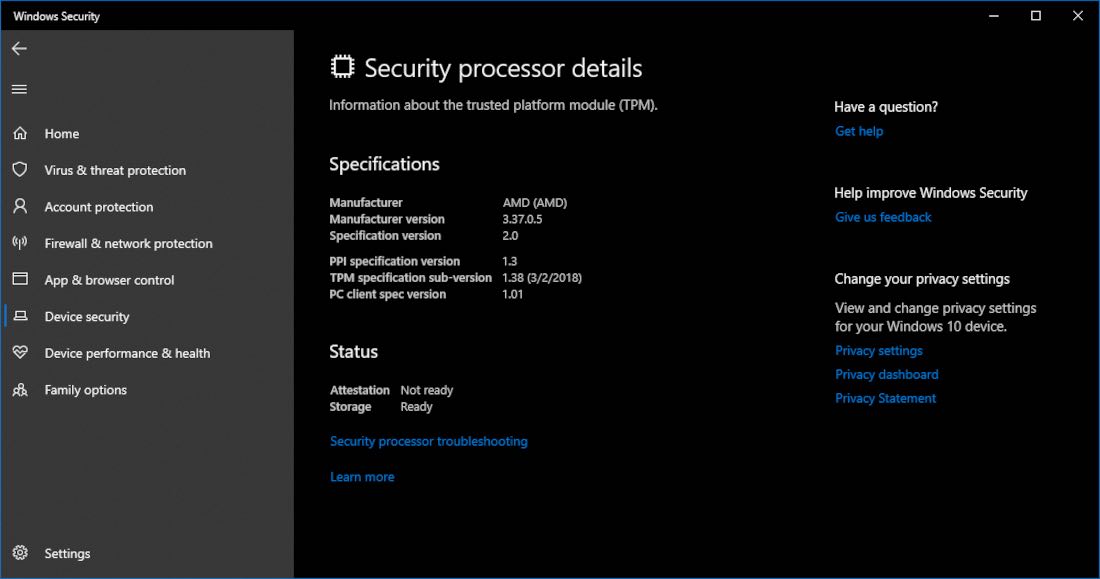
Windows 11, upon its release, introduced a significant change in system requirements: the mandatory presence of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0. While this decision aimed to enhance security and protect user data, it left many users with older hardware unable to upgrade. This sparked a wave of interest in methods to circumvent the TPM requirement, with GitHub becoming a focal point for discussions and potential solutions.
Understanding the TPM and its Role in Windows 11
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated hardware chip embedded in the motherboard of a computer. It serves as a secure cryptographic key storage and management system, playing a crucial role in securing the boot process and protecting sensitive data. In the context of Windows 11, the TPM 2.0 is a key requirement for several reasons:
- Enhanced Boot Security: The TPM verifies the integrity of the operating system and ensures that it has not been tampered with. This helps prevent malware from hijacking the boot process and gaining unauthorized access to the system.
- Secure Storage for Encryption Keys: The TPM can securely store encryption keys used for data protection. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information, even if the system is compromised.
- Stronger Authentication: The TPM can be used to enable hardware-based authentication, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to the system.
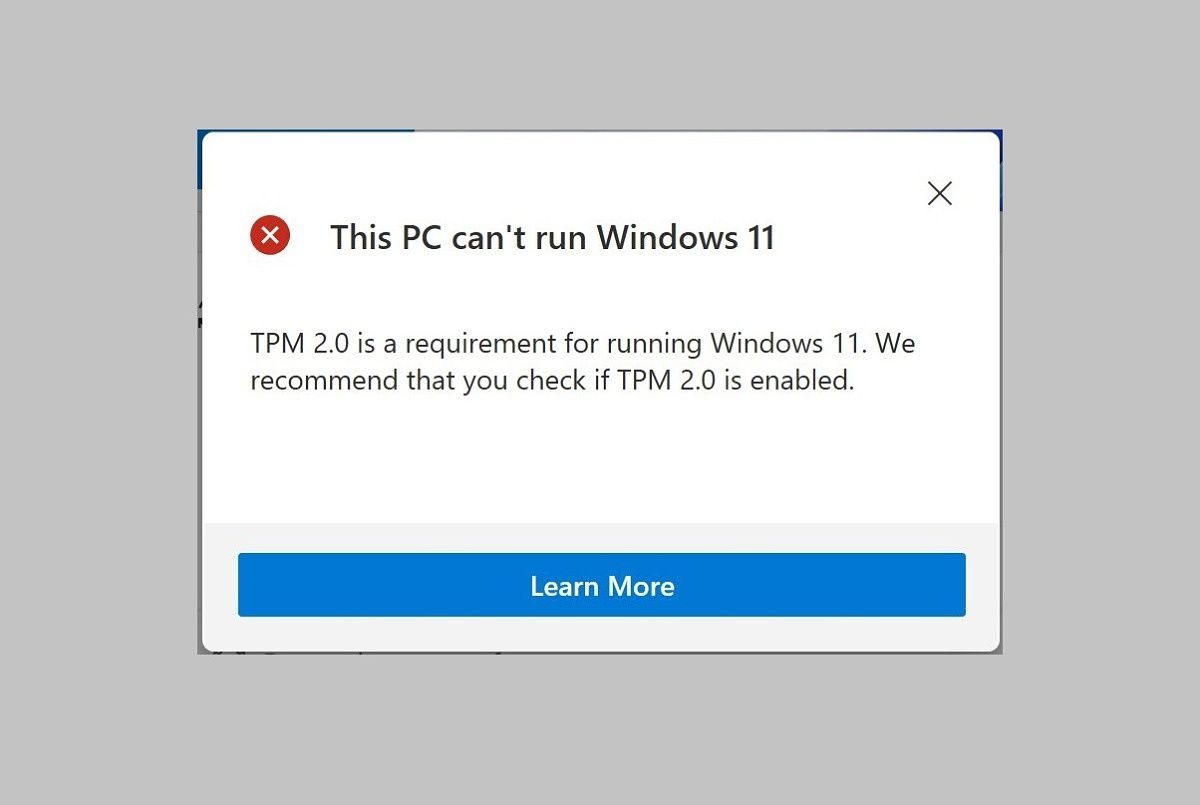
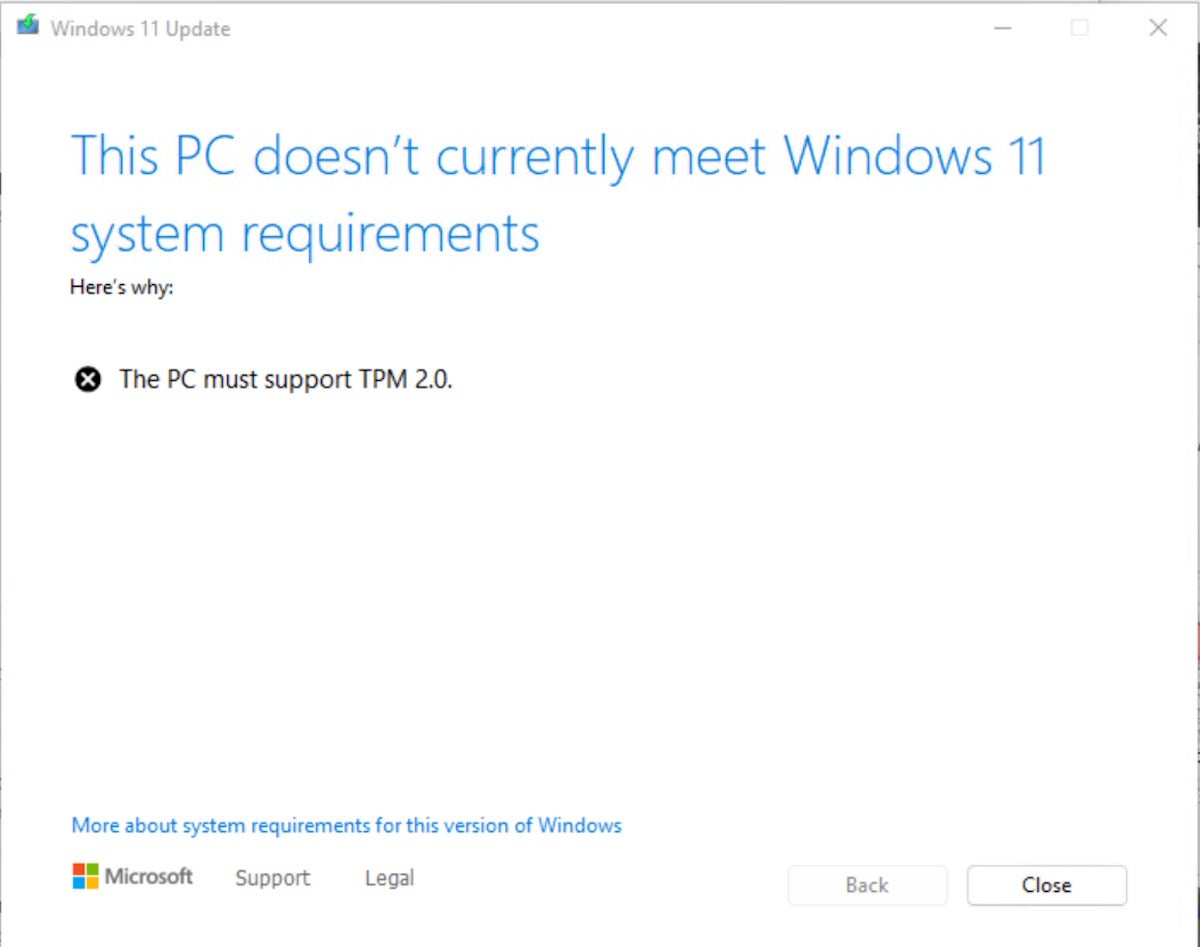
Windows 11 Compatibility: The TPM Requirement and its Implications
The mandatory TPM 2.0 requirement for Windows 11 has generated both support and criticism. While proponents argue that it strengthens security and safeguards user data, opponents highlight the potential exclusion of users with older hardware. This has led to discussions about accessibility and the potential for digital divide.
Exploring Workarounds: The Role of GitHub and Community Efforts
Given the limitations imposed by the TPM requirement, various workarounds have emerged, with GitHub serving as a platform for sharing information and potential solutions. These workarounds typically involve:
- TPM Emulation: Some solutions aim to emulate a TPM 2.0 chip through software, allowing systems without a physical TPM to meet the requirement. These methods often rely on virtualized environments or specialized software that mimics the functionality of a physical TPM.
- Registry Modifications: Certain registry modifications can temporarily disable the TPM requirement, allowing users to install Windows 11 without a compatible TPM. However, it is important to note that such modifications may compromise system security and are not officially supported by Microsoft.
- Alternative Installation Methods: Some users have reported success installing Windows 11 through alternative methods, such as using a bootable USB drive or bypassing the installation checks entirely. However, these methods often require advanced technical knowledge and may not be suitable for all users.
Important Considerations: Risks and Limitations
It is crucial to understand that bypassing the TPM requirement, while potentially enabling a Windows 11 installation on incompatible hardware, comes with inherent risks and limitations:
- Security Compromises: Bypassing the TPM can weaken system security, leaving the system vulnerable to malware and unauthorized access.
- Lack of Official Support: Microsoft does not officially support any methods for bypassing the TPM requirement. This means that users may encounter compatibility issues or lack of support from Microsoft if they encounter problems with their installation.
- Potential for Data Loss: Modifying the system’s core components, such as the registry, can lead to data loss or system instability.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns and Questions
1. Is it safe to bypass the TPM requirement?
No, bypassing the TPM requirement can compromise system security and is not recommended. It is best to ensure your hardware meets the official system requirements for Windows 11.
2. What are the benefits of having a TPM?
A TPM enhances system security by providing secure storage for encryption keys, verifying the integrity of the operating system, and enabling hardware-based authentication.
3. Can I install Windows 11 on my older computer without a TPM?
Officially, no. Windows 11 requires a TPM 2.0 for installation. However, there are workarounds available, but they are not recommended due to security risks.
4. Is it possible to upgrade my existing Windows 10 installation to Windows 11 without a TPM?
No, Windows 11 requires a TPM 2.0 for both installation and upgrade.
5. What are the alternatives to bypassing the TPM requirement?
If your hardware does not meet the requirements, consider upgrading to a system with a compatible TPM, using a virtual machine with a TPM enabled, or sticking with Windows 10.
Tips for Navigating the TPM Requirement
- Check System Requirements: Before attempting to install Windows 11, ensure your hardware meets the official system requirements.
- Consider System Upgrade: If your current hardware does not meet the requirements, consider upgrading to a system with a TPM 2.0.
- Explore Virtualization: Virtual machines can offer a workaround for users with incompatible hardware.
- Stay Informed: Keep an eye on updates and announcements from Microsoft regarding TPM requirements and potential changes.
- Seek Expert Assistance: If you are unsure about the TPM requirement or have questions about compatibility, consult a qualified technical expert.
Conclusion: Balancing Security and Accessibility
The TPM requirement in Windows 11 highlights the ongoing debate between security and accessibility. While the TPM enhances security, it can also create barriers for users with older hardware. It is important to weigh the benefits of enhanced security against the potential exclusion of users and to explore alternative solutions that prioritize both security and accessibility. As technology evolves, it is crucial for operating systems to strike a balance between security advancements and ensuring that they remain accessible to a wide range of users.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the TPM Requirement: An Exploration of Windows 11 Compatibility and Workarounds. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
