Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Related Articles: Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware

Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system, unveiled in 2021, promised a significant leap forward in user experience and security. However, its release was accompanied by a controversial decision: a stringent set of hardware requirements that effectively barred many existing computers from upgrading. This sparked widespread debate and left many users wondering if their beloved machines were destined for obsolescence.
This article delves into the complexities surrounding Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, exploring the technical reasons behind Microsoft’s decision, the potential risks and benefits of bypassing the restrictions, and the various methods users can employ to achieve compatibility.
The Technical Rationale: A Security-Driven Approach
Microsoft’s decision to restrict Windows 11 to specific hardware configurations was primarily driven by security and performance considerations. The company sought to ensure that the new operating system ran smoothly and efficiently, while simultaneously bolstering its security posture against emerging threats.
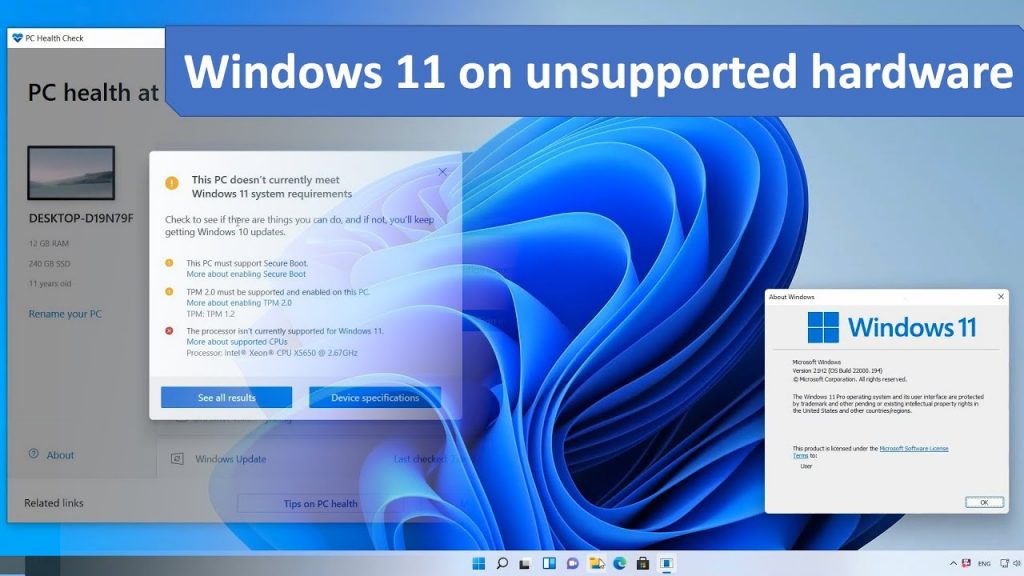
The minimum hardware requirements for Windows 11 include:
- Processor: 1 GHz or faster with 2 or more cores
- RAM: 4 GB
- Storage: 64 GB
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module 2.0
- Display: High Definition (720p) or greater, 8-bit color
- Internet Connectivity: Required for initial setup and some features
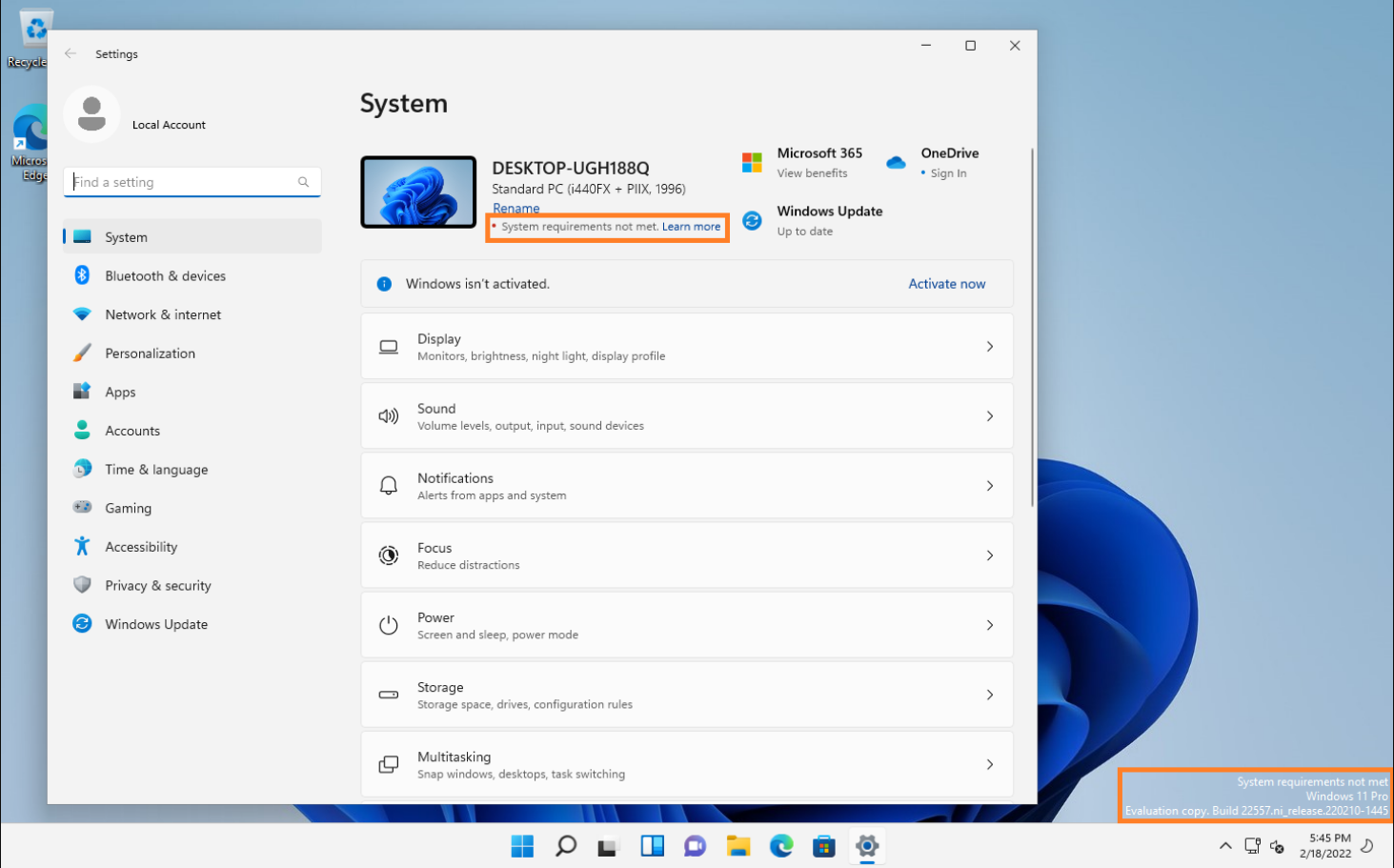
While these specifications may seem modest, they represent a significant leap forward from the requirements for Windows 10. Notably, the inclusion of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot capabilities underscores Microsoft’s commitment to enhanced security, as these features prevent malicious software from loading at boot time.
The Dilemma of Unsupported Hardware: A Balancing Act
While Microsoft’s security-focused approach is commendable, it comes at the cost of excluding a vast number of perfectly functional computers. Many users, especially those with older machines, found themselves unable to upgrade to Windows 11, forcing them to consider either purchasing new hardware or remaining on Windows 10.
This situation has led to a heated debate, with users expressing frustration at being left behind and manufacturers facing pressure to address the issue. The decision has also raised concerns about the sustainability of technology and the potential for unnecessary electronic waste.
Beyond the Official Gates: Exploring the Options
Despite Microsoft’s official stance, several methods have emerged for users to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware. These methods, while not officially sanctioned, offer potential pathways to upgrade, albeit with potential risks and caveats.
1. The Registry Tweak:
One common approach involves modifying the Windows Registry to bypass the system’s hardware checks. This method, however, requires a certain level of technical expertise and carries the risk of damaging the operating system if not performed correctly.
2. The ISO Image:
Users can download the Windows 11 ISO image directly from Microsoft’s website and perform a clean installation on their unsupported hardware. This method allows for greater control over the installation process but may require additional drivers to be installed manually.
3. Third-Party Tools:
Several third-party tools claim to enable Windows 11 installation on unsupported hardware. These tools, however, come with varying levels of reliability and may introduce security risks. Users should exercise caution and thoroughly research any tool before employing it.
4. The "Windows 11 Compatibility Update":
In an attempt to address the growing frustration, Microsoft released a "Windows 11 Compatibility Update" for Windows 10 machines that do not meet the minimum requirements. This update does not fully enable Windows 11 but aims to improve the compatibility and performance of existing systems.
The Risks and Rewards: Weighing the Options
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, while technically feasible, comes with inherent risks that users must carefully consider. These risks include:
- Security vulnerabilities: Unsupported hardware may lack the security features present in newer systems, potentially exposing the user to malware and other threats.
- Performance issues: The operating system may not function optimally on older hardware, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and other performance problems.
- Driver compatibility: Older hardware may not have compatible drivers for Windows 11, resulting in device malfunctions and limited functionality.
- Software compatibility: Some software applications may not be compatible with Windows 11, limiting the user’s functionality.
On the other hand, installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware also offers potential benefits:
- Extended lifespan for existing hardware: Users can breathe new life into their older computers, extending their usability and reducing the need for new purchases.
- Access to new features and functionalities: Windows 11 offers a range of new features and improvements, including a redesigned interface, enhanced security, and improved performance.
- Cost savings: By avoiding the expense of purchasing new hardware, users can save money while still enjoying the benefits of a newer operating system.
The Importance of Informed Decisions:
Ultimately, the decision to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware is a personal one. Users must carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits, considering their technical expertise, security concerns, and budget constraints.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What are the specific hardware requirements for Windows 11?
A: The minimum requirements for Windows 11 include a 1 GHz or faster processor with 2 or more cores, 4 GB of RAM, 64 GB of storage, UEFI with Secure Boot capability, TPM 2.0, a high-definition display, and internet connectivity.
Q: Is it safe to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware carries security risks, as older hardware may lack essential security features. Additionally, performance and compatibility issues may arise.
Q: What are the potential benefits of installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: Potential benefits include extending the lifespan of existing hardware, accessing new features and functionalities, and saving money by avoiding the purchase of new hardware.
Q: Are there any legal implications for installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: While Microsoft does not officially support installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, there are no known legal implications for doing so. However, users should be aware of the potential risks involved.
Q: What are some tips for installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: Ensure a thorough understanding of the risks involved, back up important data, research and use reputable third-party tools, and consider the potential need for additional drivers.
Conclusion: A Balancing Act for the Future
The debate surrounding Windows 11 on unsupported hardware highlights the complex interplay between technological advancements, user expectations, and corporate decisions. While Microsoft’s emphasis on security and performance is understandable, the exclusion of a significant portion of existing hardware raises concerns about accessibility, sustainability, and the overall lifecycle of technology.
As the technology landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for manufacturers and operating system developers to strike a balance between innovation and inclusivity. This balance will require a commitment to providing users with clear and transparent information, developing more flexible upgrade paths, and ensuring that new technologies are accessible to a wider range of devices. Only then can we truly unlock the potential of new operating systems while respecting the valuable resources already in our possession.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
