Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide

Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system introduced a new security measure that has sparked significant debate: the requirement for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip. This requirement, designed to enhance system security and safeguard sensitive data, has presented challenges for users with older hardware lacking this feature. While Microsoft emphasizes the importance of TPM for robust security, the need to upgrade hardware or find alternative solutions has raised concerns about accessibility and user choice.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Windows 11 TPM requirement, exploring its implications, potential workarounds, and the ongoing discussion surrounding its implementation.
Understanding the TPM and its Role in Windows 11
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized hardware chip embedded on a computer’s motherboard. It acts as a dedicated security co-processor, designed to protect sensitive data and ensure system integrity. TPM chips are certified by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG), ensuring adherence to standardized security protocols.
In the context of Windows 11, the TPM plays a crucial role in enhancing security features. Here’s how:
- Secure Boot: TPM facilitates secure boot, a process that ensures only authorized operating systems and drivers are loaded during startup. This helps prevent malware from hijacking the boot process and compromising the system.
- Data Encryption: TPM can be used to encrypt sensitive data, such as passwords and encryption keys, providing an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Hardware Authentication: TPM allows for secure hardware authentication, ensuring the integrity of the system’s components and detecting any tampering or unauthorized modifications.
The Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Controversial Decision
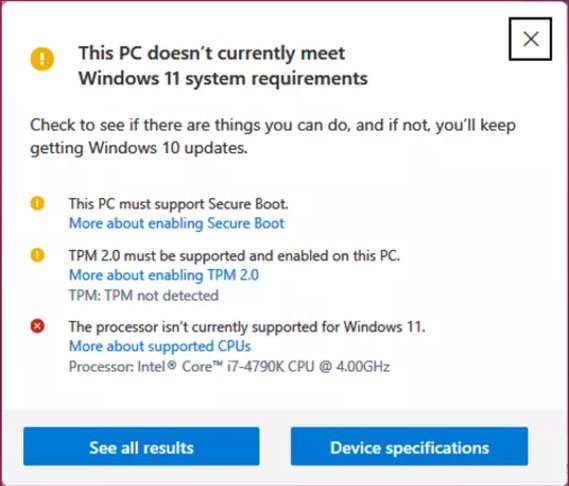
While the intention behind the TPM requirement is commendable, its implementation has faced criticism. The primary concern revolves around the accessibility of TPM 2.0 equipped hardware, particularly for users with older computers. Many users have found themselves unable to upgrade to Windows 11 due to the lack of a TPM chip in their systems.
This has fueled a debate about the necessity of the TPM requirement, with some arguing that it creates unnecessary barriers to adoption and excludes users with older, perfectly functional hardware. Others, however, maintain that the security benefits outweigh the inconvenience, emphasizing the importance of robust security measures in today’s digital landscape.
Exploring Workarounds: Bypassing the TPM Requirement
Despite Microsoft’s stance on the TPM requirement, various workarounds have emerged, allowing users to install Windows 11 on systems lacking a TPM 2.0 chip. These methods, however, come with caveats and potential security risks:
- Registry Modification: A common workaround involves modifying the Windows registry to bypass the TPM check during installation. This method, while technically effective, is not recommended due to its potential for system instability and security vulnerabilities.
- TPM Emulation: Some third-party software tools claim to emulate a TPM chip, allowing Windows 11 to install on unsupported hardware. However, the effectiveness and security implications of such tools remain unclear, and their use should be approached with caution.
- Using a Virtual Machine: Installing Windows 11 within a virtual machine environment, such as VirtualBox or VMware, can circumvent the TPM requirement. However, this approach requires additional resources and may impact performance.
The Future of the TPM Requirement: A Balancing Act
The debate surrounding the Windows 11 TPM requirement is likely to continue. While Microsoft remains committed to its security benefits, the need to balance security with accessibility remains a critical concern. It is crucial to consider the following:
- Hardware Accessibility: The availability of affordable hardware with TPM 2.0 compatibility is essential to ensure a smooth transition for users.
- User Choice and Flexibility: Providing users with options and flexibility in their choice of operating systems, regardless of hardware limitations, is crucial.
- Transparency and Communication: Clear communication from Microsoft regarding the TPM requirement and its implications, along with potential alternative solutions, is vital for user understanding and acceptance.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Is a TPM 2.0 chip absolutely necessary for Windows 11?
A: Microsoft officially requires a TPM 2.0 chip for Windows 11 installation. However, workarounds exist, although they are not officially supported and may pose security risks.
Q: What are the security benefits of using a TPM?
A: TPM enhances system security by providing secure boot, data encryption, and hardware authentication, making it more difficult for malware to compromise the system.
Q: Can I upgrade my existing computer to have a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: Most modern motherboards include a TPM chip. If your motherboard lacks one, it might be possible to purchase a separate TPM module and install it. However, compatibility with your specific system should be verified before making a purchase.
Q: What are the risks of using workarounds to bypass the TPM requirement?
A: Workarounds may compromise system security, lead to instability, and expose your system to potential vulnerabilities. They are not officially supported by Microsoft and should be used with extreme caution.
Tips: Navigating the TPM Requirement
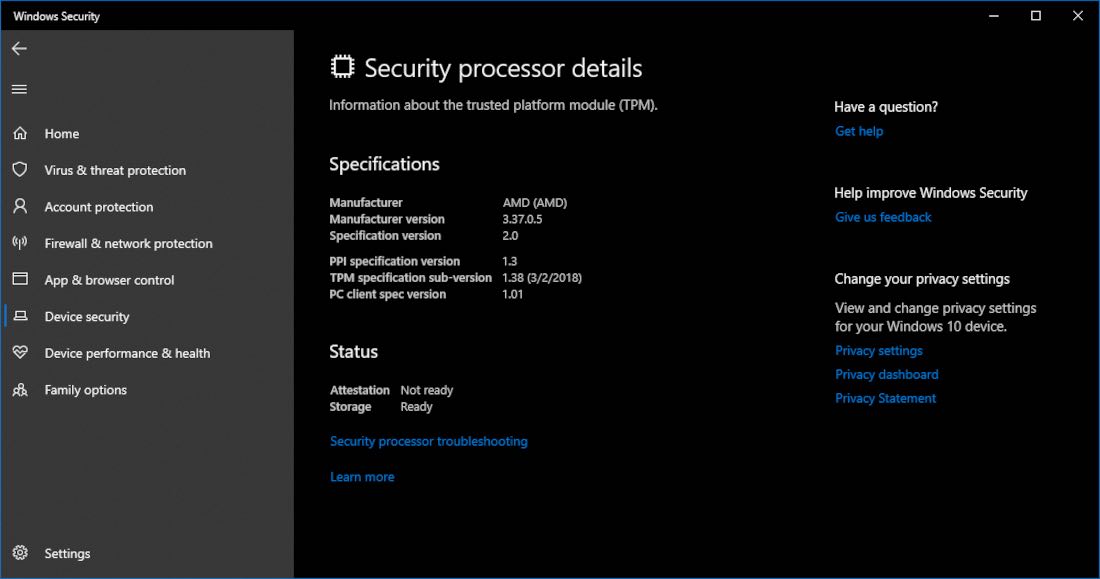
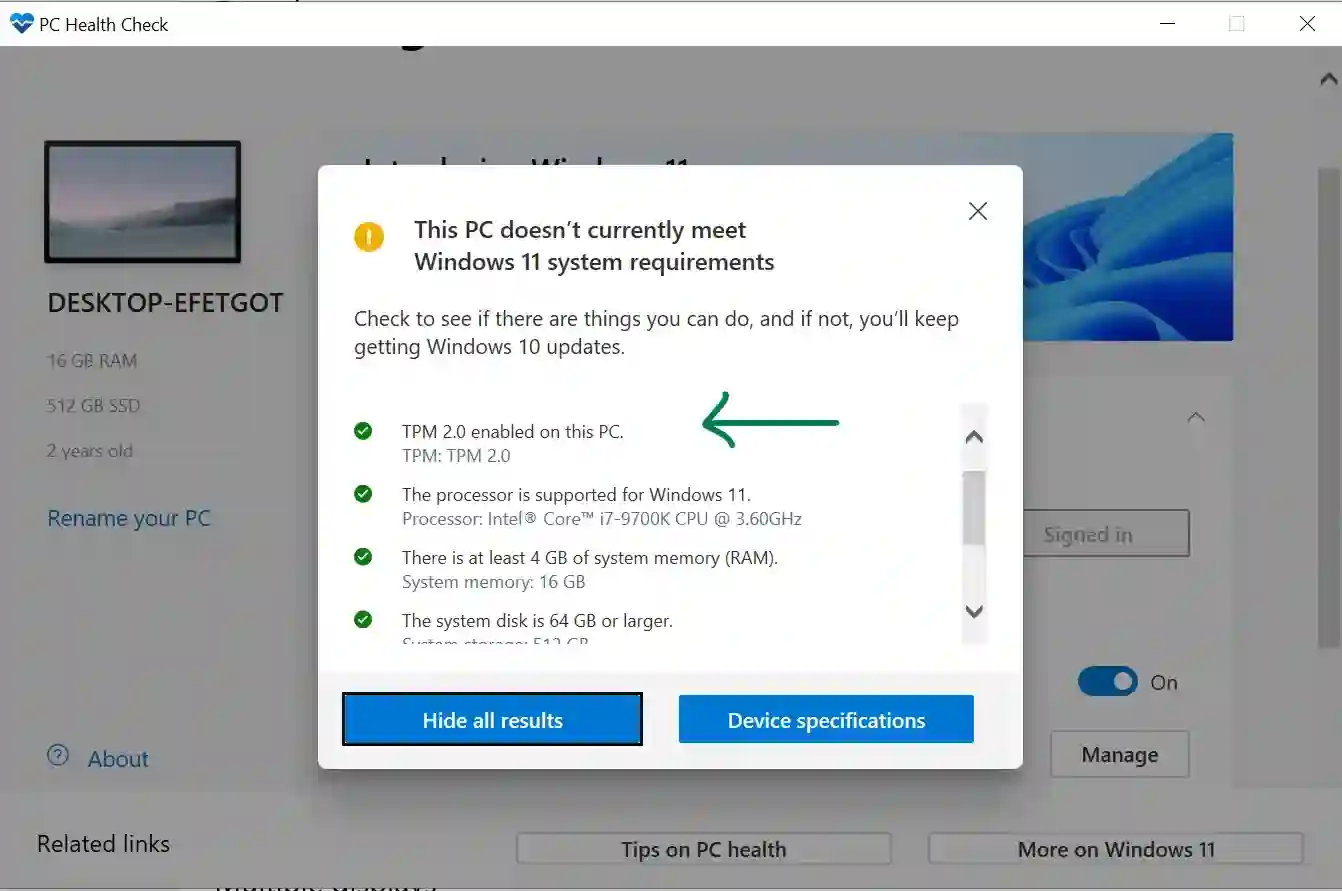
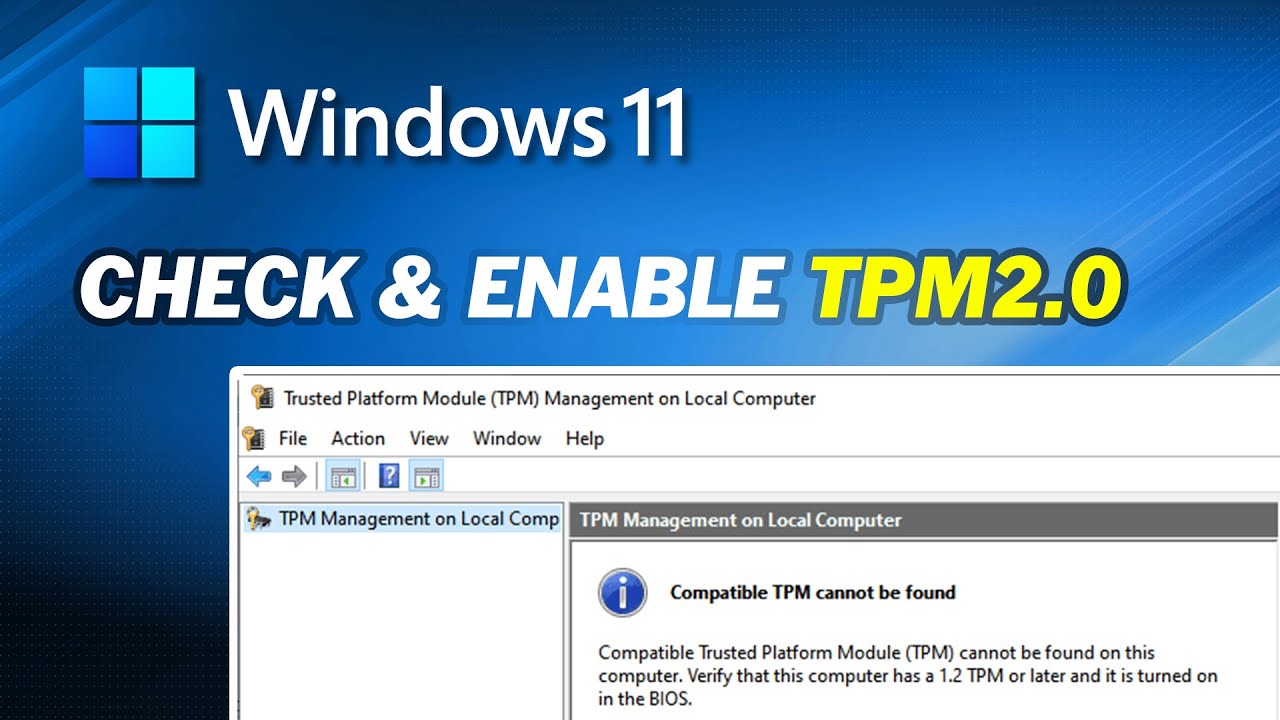
- Check for TPM Compatibility: Before upgrading to Windows 11, verify if your computer has a TPM 2.0 chip. You can use the "Windows Security" app or the "tpm.msc" command in the Run dialog box to check for TPM status.
- Consider Hardware Upgrade: If your computer lacks a TPM 2.0 chip, upgrading to a new system with TPM support might be the most secure and reliable solution.
- Explore Virtual Machines: If you’re unable to upgrade hardware, consider using a virtual machine environment to install Windows 11. This option allows you to experience the new operating system without compromising your existing system.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on the latest developments related to the TPM requirement, including potential changes to Microsoft’s policy or new workarounds that emerge.
Conclusion: A Balancing Act Between Security and Accessibility
The Windows 11 TPM requirement highlights the ongoing tension between security and accessibility in the digital world. While the security benefits of TPM are undeniable, it is crucial to ensure that these measures do not create barriers for users with older hardware or limited financial resources. Moving forward, a balance between robust security and user choice will be essential for a future where technology is accessible to all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
