Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows 11, upon its release, introduced a new set of system requirements, notably the mandate for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip. This requirement sparked debate and confusion among users, particularly those with older systems lacking this specific hardware component. While the TPM requirement aims to enhance system security, its implementation has presented a barrier for some users wishing to upgrade to Windows 11.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Windows 11 TPM requirement, exploring its purpose, implications, and alternative approaches for users facing this hurdle.
Understanding the Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
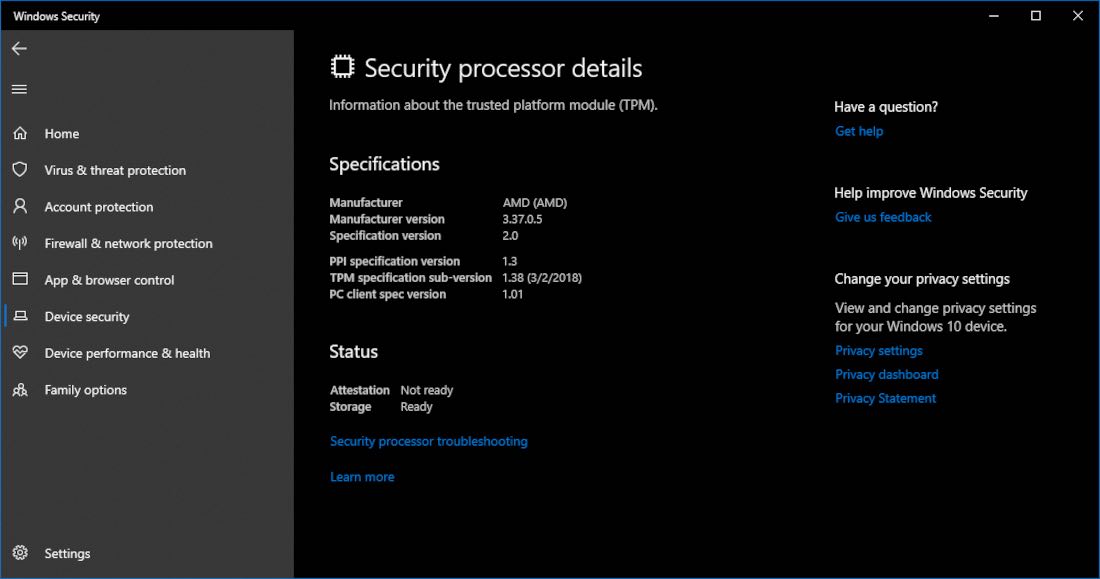
The TPM, a specialized microchip embedded within the motherboard, plays a crucial role in bolstering system security. Essentially, it functions as a hardware-based security key, safeguarding sensitive data and cryptographic operations.
Here’s a breakdown of the TPM’s key functions:
- Secure Boot: The TPM verifies the operating system’s integrity during boot-up, ensuring that only authorized software loads. This mechanism helps prevent malicious software from hijacking the boot process.
- Data Encryption: The TPM can encrypt sensitive data, such as passwords and encryption keys, preventing unauthorized access even if the system is compromised.
- Digital Signatures: The TPM enables the verification of digital signatures, guaranteeing the authenticity and integrity of software and data.
- Hardware Authentication: The TPM can be used to authenticate hardware components, ensuring that only genuine components are installed.
Why the TPM Requirement for Windows 11?
Microsoft’s decision to make the TPM 2.0 a mandatory requirement for Windows 11 stems from its commitment to enhancing system security. The TPM’s capabilities contribute to:
- Reduced Vulnerability to Malware: The secure boot feature, enabled by the TPM, significantly reduces the risk of malware infections by preventing unauthorized software from loading during startup.
- Enhanced Data Protection: The TPM’s encryption capabilities protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, even in the event of system compromise.
- Improved System Integrity: The TPM’s verification of digital signatures ensures the authenticity and integrity of software and data, mitigating the risk of malicious tampering.
Circumventing the TPM Requirement: Exploring Alternatives
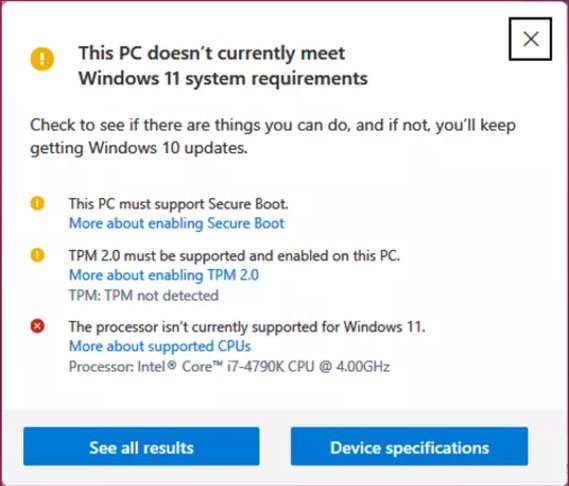
While the TPM requirement is designed to enhance security, it can pose a challenge for users with older systems lacking this hardware component. Fortunately, several alternatives exist, allowing users to install Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip.
1. Utilizing a Virtual TPM:
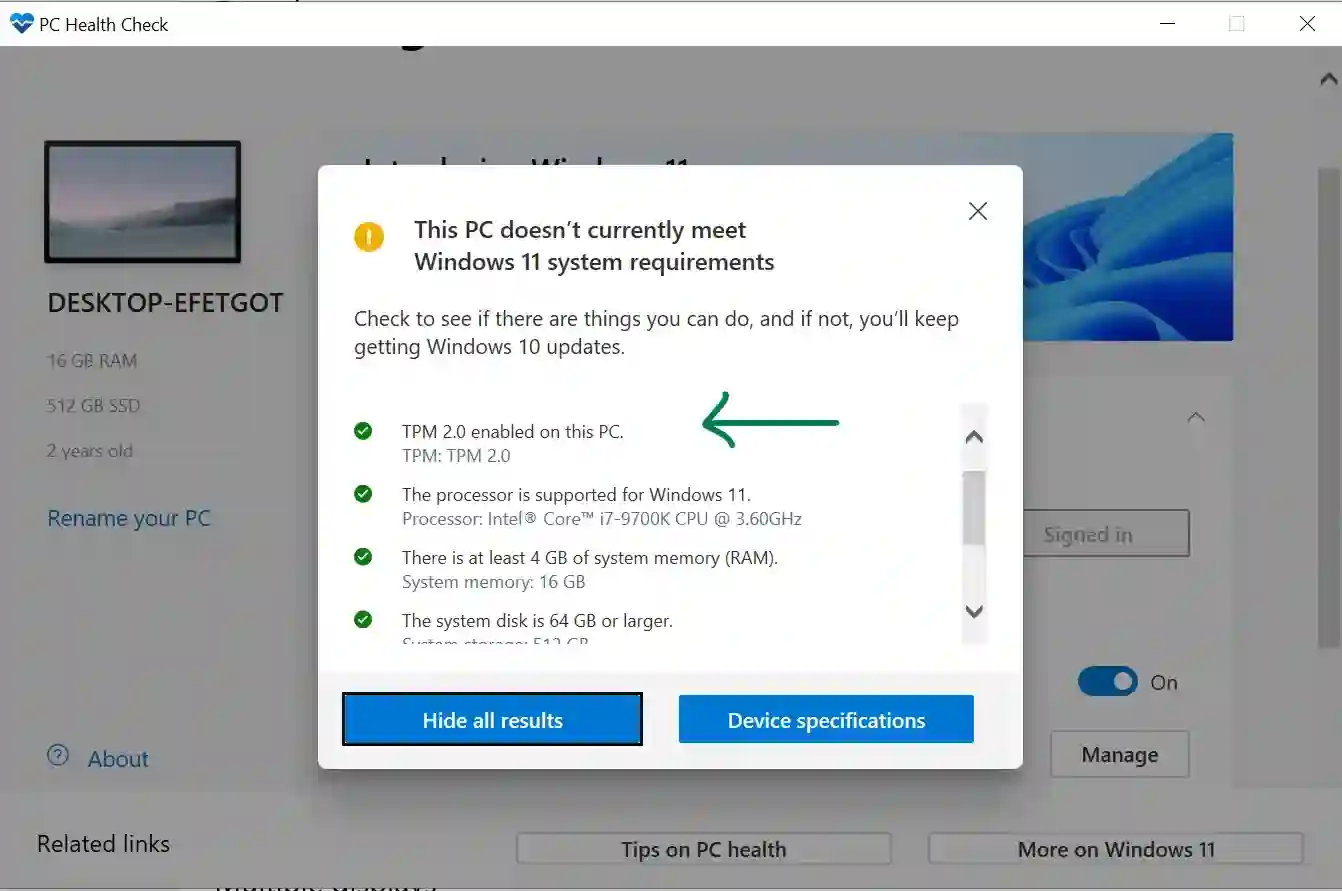
Modern motherboards often include a firmware-based TPM, also known as a fTPM, which can emulate the functionality of a dedicated TPM chip. This approach offers a software-based solution, enabling users to bypass the hardware requirement without compromising security.
2. Employing a Registry Hack:
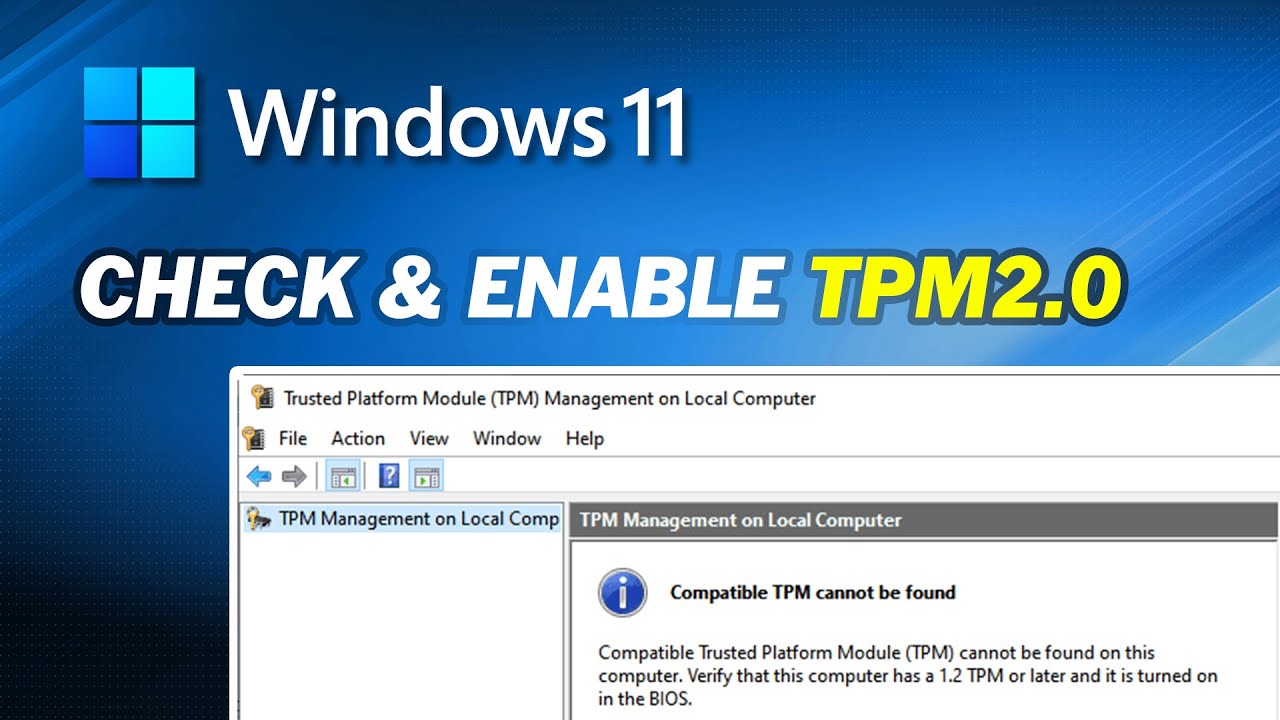
A registry hack, involving modifying specific registry entries, can temporarily circumvent the TPM requirement. However, this approach is not recommended as it can potentially destabilize the system and compromise its security.
3. Utilizing Third-Party Software:
Several third-party software solutions claim to emulate the TPM functionality, allowing users to install Windows 11 without a physical TPM. However, the reliability and security of these solutions can vary, and their use should be approached with caution.
4. Upgrading the Motherboard:
The most straightforward solution for users facing the TPM requirement is to upgrade their motherboard to one equipped with a TPM 2.0 chip. This approach provides a permanent and secure solution, ensuring compliance with Windows 11’s system requirements.
Important Considerations:
While these alternatives offer solutions for circumventing the TPM requirement, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and limitations:
- Security Implications: Bypassing the TPM requirement can compromise system security, potentially exposing the system to malware and unauthorized access.
- Software Compatibility: Software compatibility issues may arise when using alternative solutions, as they might not fully emulate the TPM’s functionality.
- System Stability: The use of registry hacks or third-party software can potentially destabilize the system, leading to performance issues or system crashes.
FAQs Regarding Windows 11 TPM Bypass:
Q: Is it safe to bypass the TPM requirement?
A: Bypassing the TPM requirement can compromise system security, potentially exposing the system to malware and unauthorized access. While alternative solutions exist, it’s essential to weigh the potential risks against the benefits.
Q: What are the consequences of bypassing the TPM requirement?
A: Bypassing the TPM requirement can result in a less secure system, making it more vulnerable to malware and data breaches. Additionally, it may lead to software compatibility issues and system instability.
Q: Are there any legal implications for bypassing the TPM requirement?
A: Bypassing the TPM requirement may violate the terms of service of Windows 11, potentially leading to software licensing issues. It’s crucial to consult the relevant terms of service and licensing agreements.
Q: What are the best practices for ensuring system security when bypassing the TPM requirement?
A: If you choose to bypass the TPM requirement, it’s essential to take extra precautions to mitigate security risks. This includes using robust antivirus software, regularly updating the operating system and software, and being cautious about downloading files from untrusted sources.
Tips for Windows 11 TPM Bypass:
- Prioritize Security: If you choose to bypass the TPM requirement, prioritize system security by employing comprehensive antivirus protection, regularly updating software, and exercising caution when browsing the internet.
- Consider Upgrading: If possible, consider upgrading your motherboard to one equipped with a TPM 2.0 chip. This provides a permanent and secure solution, ensuring compliance with Windows 11’s system requirements.
- Research Alternatives Thoroughly: Before implementing any alternative solutions, thoroughly research their reliability, security implications, and potential compatibility issues.
- Consult Technical Support: If you’re unsure about the best approach, consult with a qualified technical support professional for guidance.
Conclusion:
The Windows 11 TPM requirement reflects Microsoft’s commitment to enhancing system security, providing a hardware-based safeguard against malicious threats. While this requirement can present a challenge for users with older systems, alternative solutions exist. However, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and limitations associated with bypassing the TPM requirement. By carefully considering the available options and prioritizing system security, users can navigate the TPM requirement effectively, ensuring a smooth and secure transition to Windows 11.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 TPM Requirement: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
