Navigating the Windows 11 Update: Understanding CPU Compatibility and Potential Workarounds
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 Update: Understanding CPU Compatibility and Potential Workarounds
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 Update: Understanding CPU Compatibility and Potential Workarounds. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 11 Update: Understanding CPU Compatibility and Potential Workarounds

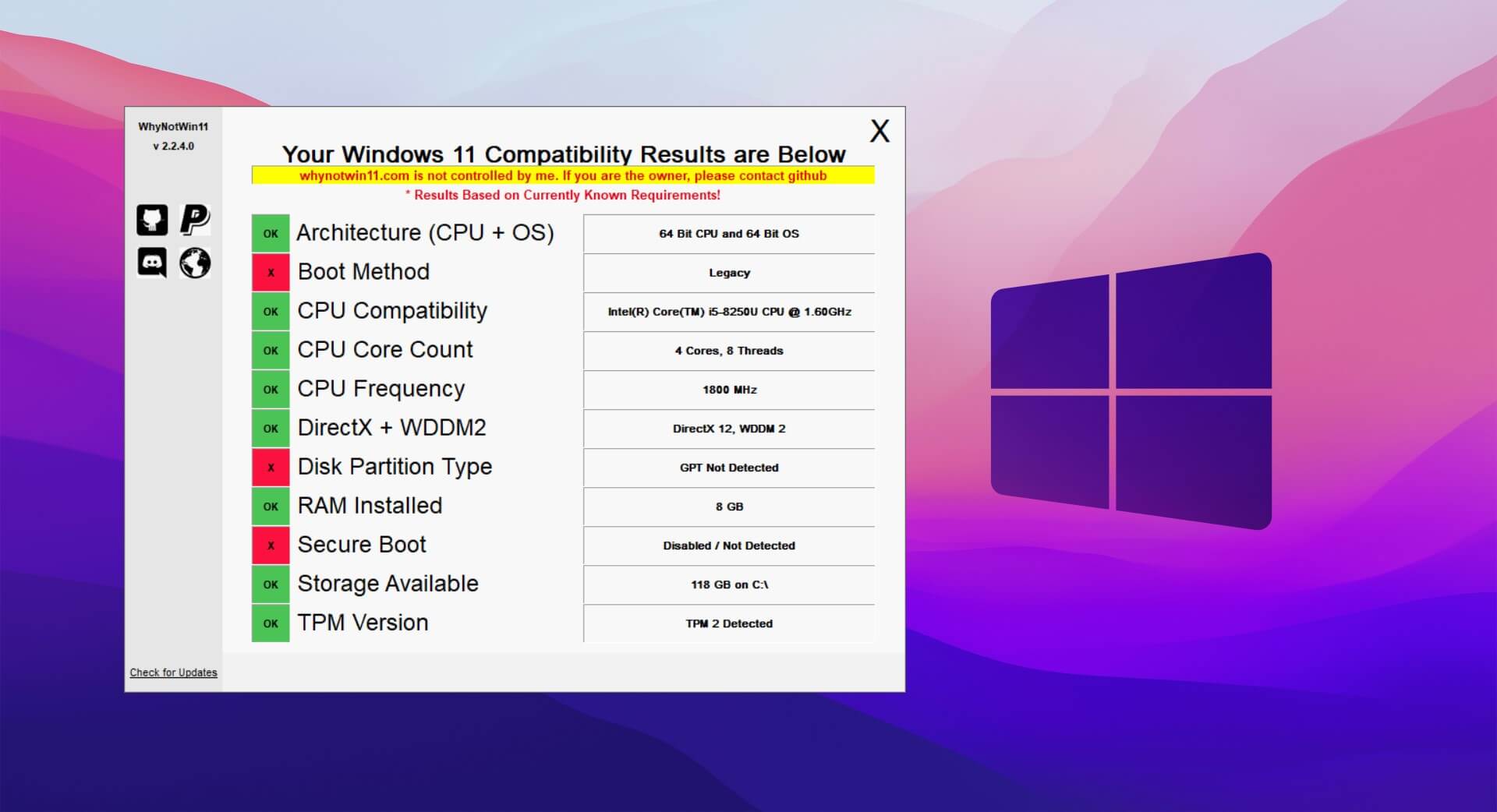
Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system, launched in 2021, brought a host of new features and design changes. However, its introduction was accompanied by a stringent requirement: a compatible processor. This requirement, aimed at ensuring optimal performance and stability, presented a hurdle for users with older computers. While Microsoft’s intention was to enhance the user experience, this CPU compatibility check, implemented through a system known as "PC Health Check," left some users unable to upgrade.
This article delves into the intricacies of the Windows 11 CPU compatibility check, exploring its rationale, implications, and potential workarounds. We will examine the reasons behind Microsoft’s decision, the limitations it imposed, and the various methods users have devised to circumvent the check.
Understanding the CPU Compatibility Check: A Security and Performance Perspective
The core of the Windows 11 CPU compatibility check lies in the desire to ensure a smooth and secure user experience. Microsoft’s reasoning for this stringent requirement stems from the following factors:
-
Security Enhancement: Modern CPUs are equipped with security features, such as "Virtualization Based Security" (VBS), that are crucial for protecting against advanced malware and cyber threats. Windows 11 leverages these features extensively, ensuring a more secure operating environment. Older processors, lacking these security features, would be susceptible to vulnerabilities, potentially compromising user data and system integrity.
-
Performance Optimization: Windows 11 is designed to take advantage of the latest hardware advancements, including faster processors and more efficient memory management. By requiring a minimum CPU capability, Microsoft aimed to guarantee a fluid and responsive user experience. Older processors, lacking the necessary processing power, might struggle to run Windows 11 effectively, leading to lag, slowdowns, and overall performance degradation.
-
Hardware Ecosystem Integration: Windows 11 is intended to seamlessly integrate with a diverse range of hardware components, including modern displays, peripherals, and networking technologies. This integration is facilitated by the compatibility of the CPU with the operating system. Older processors, lacking the necessary drivers and support for these technologies, might lead to compatibility issues and hinder the optimal functioning of the system.
The Implications of the CPU Compatibility Check: Barriers to Upgrade
While the CPU compatibility check aimed to provide a secure and optimized user experience, it inadvertently created barriers for users with older computers. The requirement effectively prevented users with non-compliant processors from upgrading to Windows 11, leaving them with an outdated operating system.
-
Limited Hardware Choice: The CPU compatibility check restricted users to a specific set of processors, limiting their hardware options. This could have significant implications for budget-conscious users or those seeking specific performance characteristics.
-
Software Compatibility Issues: Older processors might lack support for the latest software applications and games designed for Windows 11. This could limit users’ access to new features, advancements, and functionalities.
-
Security Risks: While Microsoft’s primary intention was to enhance security, the inability to upgrade to Windows 11 left users with older operating systems vulnerable to known security exploits and vulnerabilities.
Exploring Workarounds: Circumventing the CPU Compatibility Check
The stringent CPU compatibility check sparked innovation among users seeking to overcome the limitations imposed by Microsoft’s requirement. Several methods emerged, allowing users to bypass the check and install Windows 11 on non-compliant systems. However, it’s crucial to understand that these methods are not officially endorsed by Microsoft and might come with potential risks.
-
Registry Editing: This method involves manually modifying specific registry keys related to the CPU compatibility check. It requires a high level of technical expertise and should only be attempted by users with a thorough understanding of the Windows registry. Incorrect modifications can lead to system instability and data loss.
-
Using a USB Bootable Drive: Creating a bootable USB drive with the Windows 11 installation files allows users to bypass the initial compatibility check during the installation process. However, this method might still encounter issues during the post-installation setup phase.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Software: Some third-party software tools claim to circumvent the CPU compatibility check. However, these tools might be unreliable, potentially introducing malware or compromising system security.
The Importance of Informed Decision-Making
Before attempting any of these workarounds, it is essential to weigh the potential risks and benefits carefully. While the desire to upgrade to Windows 11 is understandable, it’s crucial to ensure that the chosen method is safe and does not compromise the security and stability of the system. Users should also consider the potential performance implications of running Windows 11 on a non-compliant processor.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the minimum CPU requirements for Windows 11?
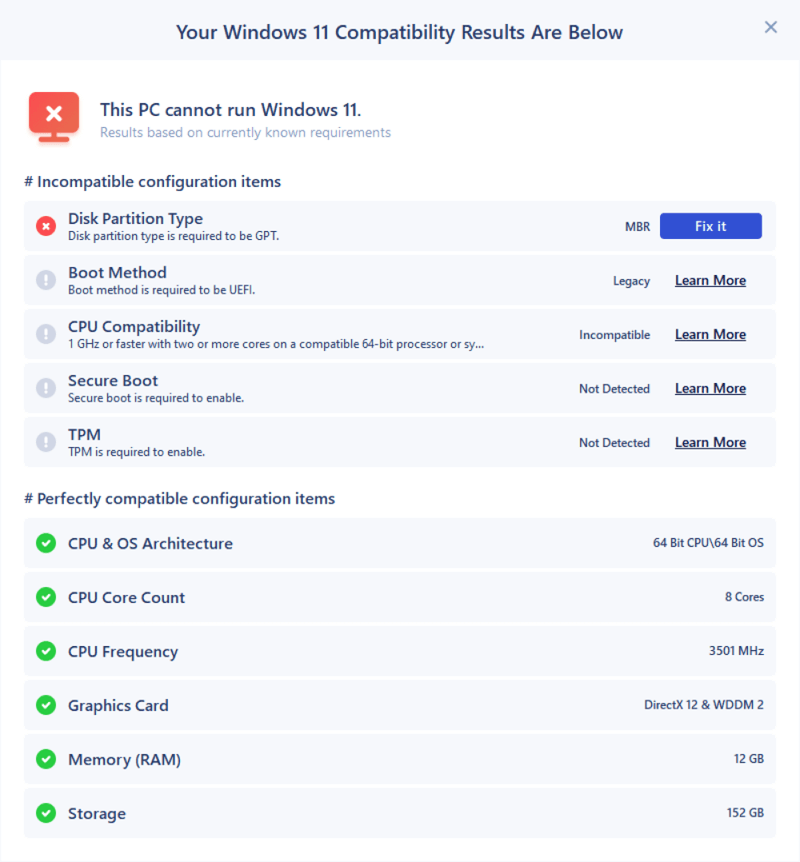
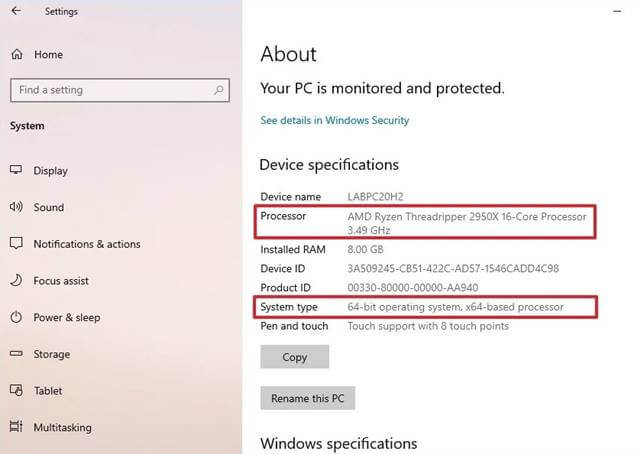
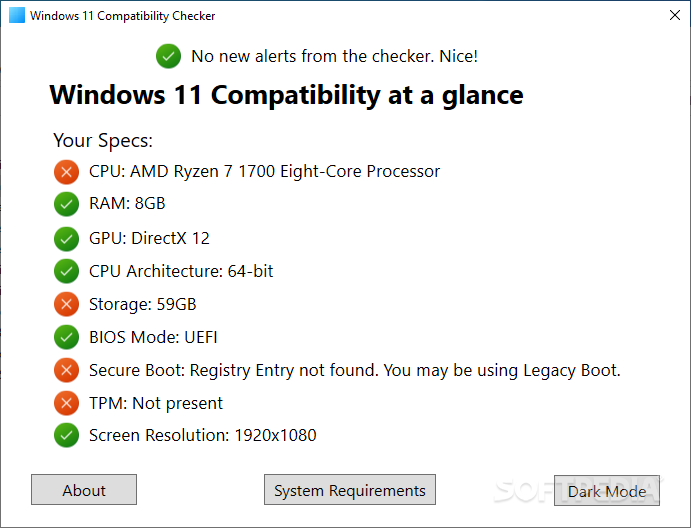
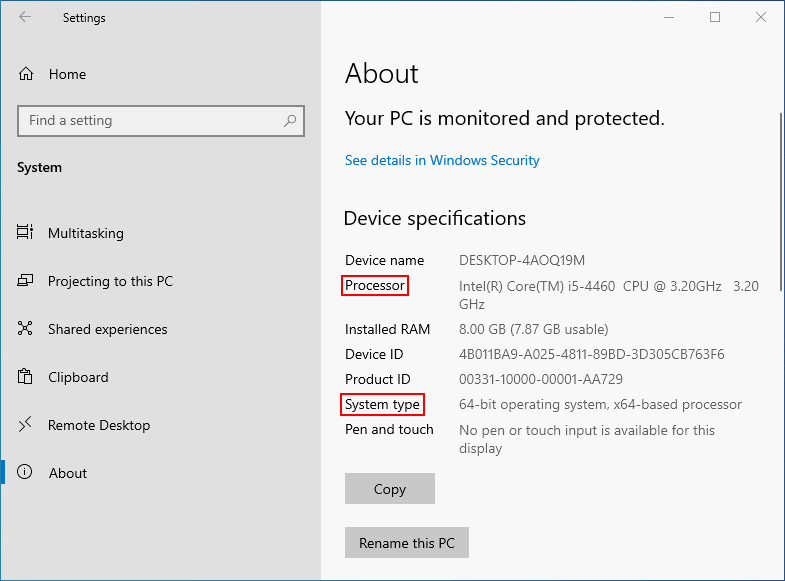
Microsoft requires a processor with at least two cores, a clock speed of 1 GHz or higher, and support for "Virtualization Based Security" (VBS).
2. Can I upgrade my existing Windows 10 system to Windows 11 without meeting the CPU requirements?
No, the CPU compatibility check is a fundamental requirement for upgrading to Windows 11.
3. Is it safe to bypass the CPU compatibility check?
While various methods exist, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks involved. Modifying system settings or using third-party software can lead to security vulnerabilities and system instability.
4. What are the performance implications of running Windows 11 on a non-compliant processor?
Running Windows 11 on a processor that doesn’t meet the minimum requirements might result in slowdowns, lag, and overall performance degradation.
5. Should I upgrade to Windows 11 if my CPU doesn’t meet the requirements?
If your CPU does not meet the minimum requirements, it’s generally recommended to remain on Windows 10. However, if you are willing to accept the potential risks and performance implications, you can explore the available workarounds.
Tips for Navigating the Windows 11 Update
-
Check CPU Compatibility: Before attempting an upgrade, ensure your CPU meets the minimum requirements. Use the "PC Health Check" tool or consult the official Windows 11 specifications.
-
Consider Performance Impact: If your CPU doesn’t meet the requirements, consider the potential performance impact of running Windows 11.
-
Prioritize Security: If you choose to bypass the compatibility check, prioritize security by using reliable methods and avoiding potentially malicious software.
-
Backup Your Data: Before making any significant system changes, create a backup of your important data to prevent potential loss.
-
Seek Expert Assistance: If you are unsure about the process or have concerns, consult a qualified IT professional for guidance.
Conclusion: Navigating the Windows 11 Upgrade Landscape
The Windows 11 CPU compatibility check, while intended to enhance user experience and security, presented a challenge for users with older computers. While workarounds exist, they come with inherent risks and potential performance implications. Users should carefully consider their options, prioritize security, and make informed decisions based on their individual needs and circumstances. Ultimately, the best course of action is to ensure that the system meets the minimum requirements for a seamless and secure Windows 11 experience. Staying informed about the latest updates and guidelines from Microsoft is crucial in navigating this evolving landscape.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 Update: Understanding CPU Compatibility and Potential Workarounds. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
