Navigating the World of Text Files in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Text Files in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Text Files in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Text Files in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

The ubiquitous nature of text files makes them an essential element in the digital landscape. From storing simple notes to facilitating complex data transfer, text files serve a multitude of purposes. Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, provides a robust environment for interacting with text files, offering users a plethora of tools and methods to manage, edit, and utilize these fundamental data structures. This article delves into the intricacies of text files in Windows 11, elucidating their significance, exploring various methods of handling them, and addressing common queries associated with their use.
Understanding Text Files: A Foundation for Digital Interaction
Text files, often denoted by the ‘.txt’ extension, are plain-text documents that store information in a simple, unformatted manner. Unlike rich-text documents, which incorporate formatting elements like bold, italics, and colors, text files solely rely on ASCII characters, allowing for easy compatibility across different operating systems and software applications. This simplicity makes them ideal for tasks like:
- Storing basic information: Notes, lists, reminders, and other brief textual data can be conveniently stored in text files.
- Data transfer: Text files serve as a reliable method for transferring information between different devices and platforms.
- Configuration files: Numerous applications utilize text files to store configuration settings and preferences, enabling users to customize their software behavior.
- Log files: System logs, error reports, and other diagnostic information are often stored in text files, providing valuable insights into software and hardware performance.
- Code development: Programmers frequently use text files to write and edit source code, leveraging the simplicity of plain text for easy readability and manipulation.
Methods for Downloading and Handling Text Files in Windows 11
Windows 11 provides a range of avenues for acquiring and managing text files, catering to diverse user needs and preferences:
1. Downloading Text Files from the Internet:
- Web Browsers: Popular browsers like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Opera seamlessly download text files from websites. Users can typically right-click on a downloadable link and select "Save Link As" or "Download Linked File" to initiate the download process.
- Dedicated Download Managers: Software like Free Download Manager, EagleGet, and JDownloader can enhance download speeds, schedule downloads, and provide advanced features like resume functionality.
- File Sharing Services: Platforms like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive offer cloud storage options that allow users to upload, download, and share text files with ease.
2. Creating Text Files in Windows 11:
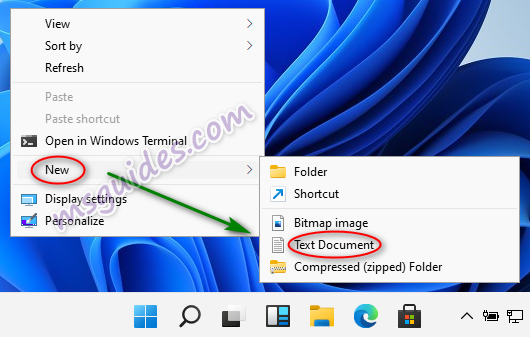
- Notepad: The built-in Notepad application provides a simple, straightforward way to create and edit text files. Users can access Notepad by searching for it in the Start menu or using the keyboard shortcut "Windows Key + R" followed by "notepad" and pressing Enter.
- WordPad: Offering slightly more functionality than Notepad, WordPad allows basic formatting options like bold, italics, and font changes. It can be accessed via the Start menu or by searching for it.
- Third-Party Text Editors: Advanced text editors like Notepad++, Sublime Text, and Atom offer robust features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and extensive customization options, making them ideal for programmers and users who require advanced text editing capabilities.
3. Opening and Editing Text Files in Windows 11:
- Default Text Editor: Windows 11 automatically associates the ‘.txt’ extension with its default text editor, usually Notepad. Double-clicking a text file will open it in the default editor.
- Changing the Default Text Editor: Users can modify the default text editor by right-clicking a text file, selecting "Open with," and choosing the desired editor from the list.
- Using the Command Prompt: The Command Prompt offers a powerful way to interact with text files using commands like "type" to display the contents, "copy" to create duplicates, and "del" to delete files.
4. Managing Text Files in Windows 11:
- File Explorer: Windows 11’s File Explorer provides a visual interface for navigating and managing files, including text files. Users can organize files into folders, rename them, and delete them using the File Explorer’s intuitive interface.
- Search Functionality: Windows 11’s search bar allows users to quickly find specific text files by name or content.
- File Properties: Right-clicking a text file and selecting "Properties" reveals information like file size, creation date, and last modified date.
Addressing Common Queries: A Guide to Troubleshooting
1. "My text file won’t open."
- File Association Issues: Ensure the ‘.txt’ extension is associated with a suitable text editor. If the file is associated with an incompatible program, it may fail to open.
- File Corruption: Damaged or corrupted text files can prevent opening. Attempting to open the file in a different text editor or using a file repair tool might resolve the issue.
- Encoding Errors: Text files can be encoded using different character sets. If the encoding of the file does not match the encoding settings of the text editor, it may appear as gibberish.
2. "My text file is empty."
- File Size: Verify the file size. An empty text file will have a size of 0 bytes.
- Hidden Characters: Some text editors may display hidden characters, such as spaces or line breaks. Ensure that these characters are not causing the file to appear empty.
- File Corruption: As mentioned earlier, file corruption can lead to empty files.
3. "My text file is too large."
- Text Editor Limitations: Some text editors may have limitations on the size of files they can handle. Consider using a different editor or splitting the file into smaller parts.
- Data Storage: If the file is exceptionally large, consider using alternative storage methods like cloud storage or databases.
4. "My text file contains special characters."
- Character Encoding: Ensure the text editor and the file use the same character encoding. Consider changing the encoding settings in the text editor to match the file’s encoding.
- Unicode Support: Modern text editors typically support Unicode, which allows for a wide range of characters. If the file uses a non-Unicode encoding, it may not display all characters correctly.
Tips for Effective Text File Management in Windows 11:
- Naming Conventions: Employ consistent and descriptive naming conventions for text files to facilitate organization and retrieval.
- Folder Structure: Organize text files into logical folders based on their purpose or content.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up important text files to prevent data loss due to hardware failures or accidental deletions.
- Cloud Storage: Utilize cloud storage services to synchronize text files across multiple devices and access them from anywhere.
- Text Editor Selection: Choose a text editor that meets your specific needs, whether for basic editing, code development, or advanced formatting.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Text Files in Windows 11
Text files remain indispensable components of the digital landscape, serving as fundamental building blocks for data storage, transfer, and communication. Windows 11 offers a comprehensive environment for managing text files, providing users with a range of tools and methods to create, edit, and utilize these essential data structures. By understanding the nuances of text files and leveraging the capabilities of Windows 11, users can efficiently harness their power to enhance productivity and streamline digital workflows.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Text Files in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
