Navigating Windows 11: The TPM Requirement and Beyond
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11: The TPM Requirement and Beyond
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11: The TPM Requirement and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11: The TPM Requirement and Beyond

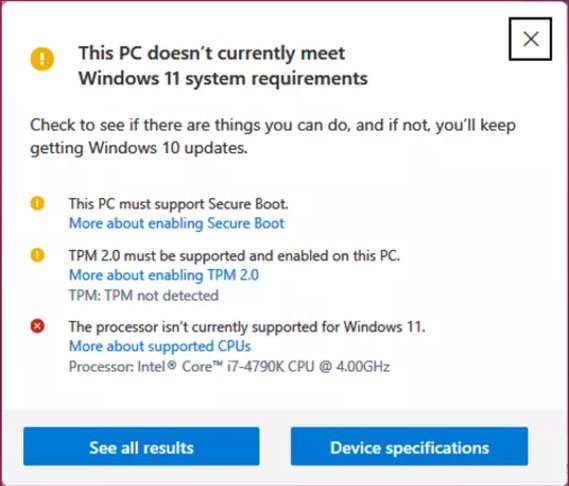
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, has ushered in a new era of computing with its sleek design, enhanced security features, and improved performance. However, its implementation has been met with some controversy due to the requirement for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip. This requirement, intended to bolster security, has presented a barrier for users with older hardware, prompting questions about compatibility and the overall impact on the user experience.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Windows 11’s TPM requirement, exploring its significance, potential workarounds, and the implications for users seeking to upgrade their systems.
Understanding the Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
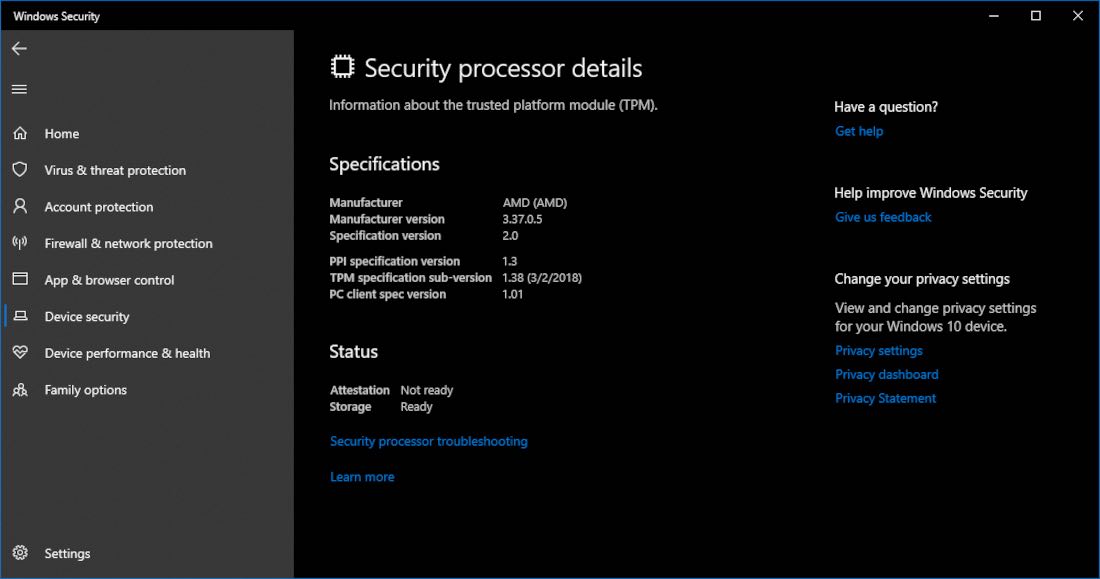
The TPM is a specialized hardware component embedded within a computer’s motherboard. It functions as a secure cryptographic processor, responsible for generating and storing cryptographic keys, verifying system integrity, and protecting sensitive data. The TPM 2.0 standard, introduced in 2015, offers enhanced security features over its predecessor, TPM 1.2.
Windows 11 and the TPM Requirement
Microsoft’s decision to mandate TPM 2.0 for Windows 11 was driven by the desire to strengthen system security and protect against evolving threats. A TPM 2.0 chip provides a robust foundation for:
- Secure Boot: This feature ensures that only trusted software, verified by the TPM, is allowed to load during system startup. This mitigates the risk of malware or unauthorized code compromising the operating system.
- Disk Encryption: The TPM can be used to encrypt the entire system drive, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. This is especially crucial for users handling confidential information or working in environments with stringent data security regulations.
- Password Management: TPMs can securely store and manage user credentials, enhancing password security and reducing the risk of credential theft.
- Hardware-Based Security: The TPM’s dedicated hardware architecture provides a secure environment for cryptographic operations, making it more difficult for attackers to tamper with security mechanisms.
Navigating the TPM Requirement: Workarounds and Solutions
While the TPM requirement is designed to enhance security, it can pose a challenge for users with older systems lacking the necessary hardware. There are, however, several workarounds and solutions to consider:
- TPM Emulation: Certain motherboards, even without a dedicated TPM chip, might offer TPM emulation through firmware updates. This allows the system to simulate a TPM environment, potentially enabling Windows 11 installation. However, it’s important to note that TPM emulation might not offer the same level of security as a dedicated TPM chip.
- BIOS Updates: Updating the system’s BIOS, which manages the hardware, can sometimes enable TPM functionality. This involves checking the manufacturer’s website for the latest BIOS updates and following the provided instructions carefully.
- Windows 11 Installation Media Modification: It is possible to modify the Windows 11 installation media to bypass the TPM requirement. However, this method is not recommended as it can compromise system security and potentially lead to instability.
- Alternative Operating Systems: If upgrading to Windows 11 proves impossible due to the TPM requirement, users can explore alternative operating systems like Linux distributions, which generally do not require a TPM. These systems offer a wide range of applications and a robust security framework, often tailored for specific user needs.
- Hardware Upgrade: The most straightforward solution is to upgrade to a newer system that includes a TPM 2.0 chip. This ensures full compatibility with Windows 11 and provides the highest level of security.
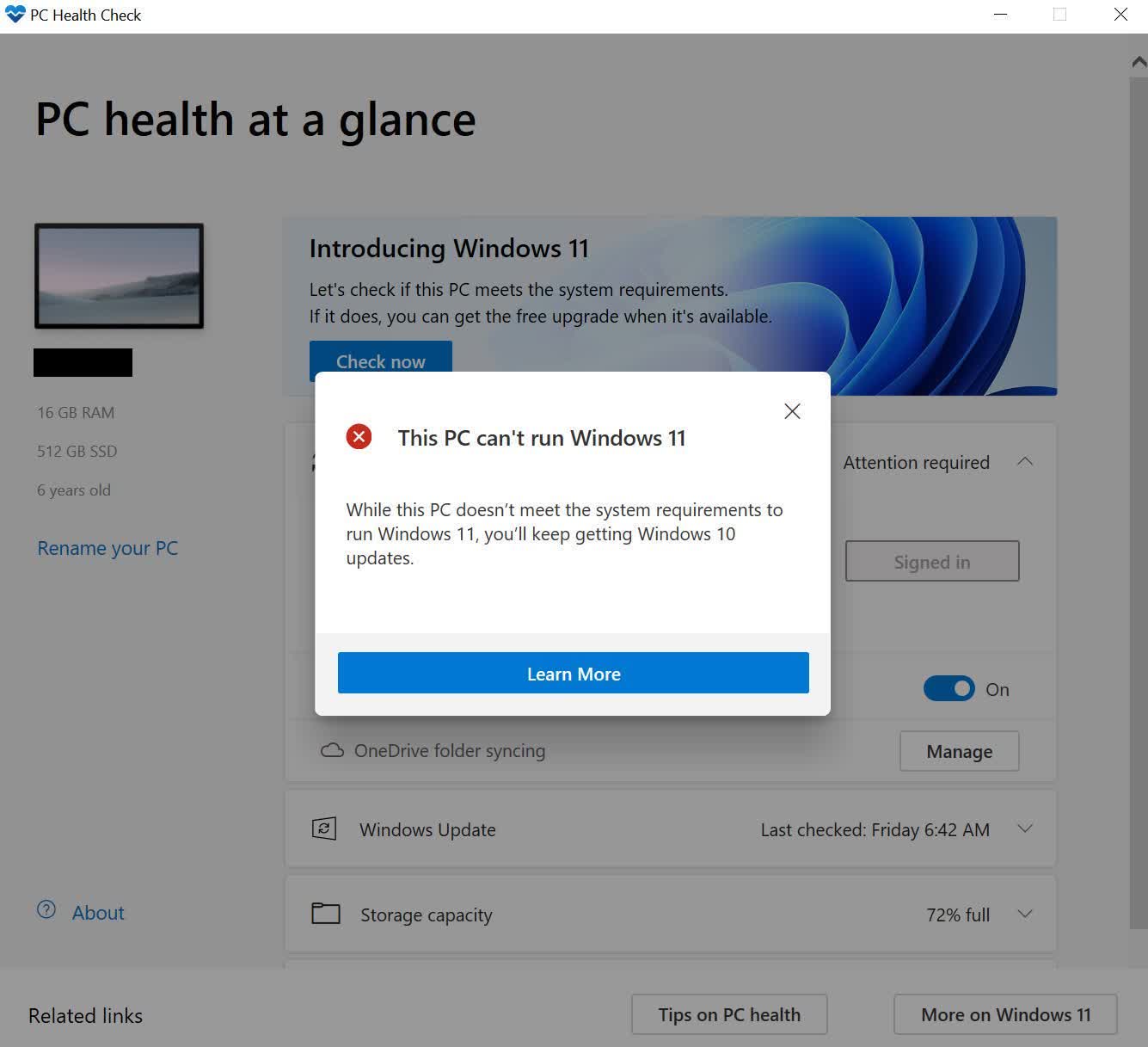
Considerations for Users with Older Systems
For users with older computers lacking a TPM 2.0 chip, the decision to upgrade to Windows 11 requires careful consideration. While the operating system offers compelling features, the lack of a TPM might compromise security and potentially lead to compatibility issues.
It is crucial to assess the specific needs and security requirements of each user. If the system is primarily used for basic tasks and does not handle sensitive data, the lack of a TPM might not pose a significant risk. However, for users handling confidential information or working in environments with stringent security standards, upgrading to a system with a TPM 2.0 chip is highly recommended.
The Importance of Security in the Modern Computing Landscape
The increasing prevalence of cyberattacks and data breaches underscores the importance of robust security measures in today’s digital landscape. The TPM requirement in Windows 11 reflects Microsoft’s commitment to protecting user data and ensuring a secure computing environment.
While the requirement might present challenges for users with older hardware, it ultimately aims to safeguard systems against evolving threats and promote responsible data management practices.
FAQs about Windows 11 and the TPM Requirement:
Q: Is a TPM 2.0 chip absolutely necessary for Windows 11?
A: While Microsoft officially recommends a TPM 2.0 chip for Windows 11, it’s not strictly mandatory. Certain workarounds and solutions exist, but they might not offer the same level of security as a dedicated TPM chip.
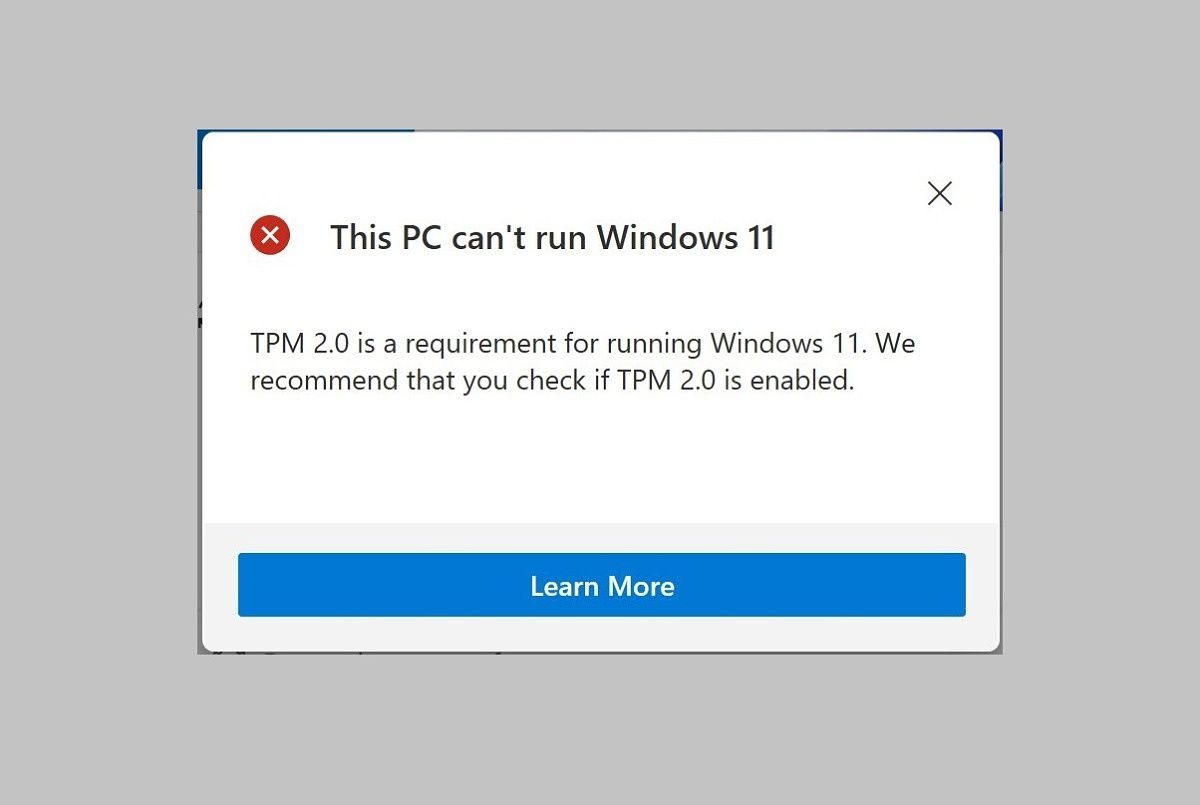
Q: Can I install Windows 11 on a computer without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: It is possible to install Windows 11 on a system without a TPM 2.0 chip, but it is not recommended. The installation process might involve bypassing security measures, potentially compromising system integrity and security.
Q: What are the risks of using Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: Using Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip might increase the vulnerability of the system to malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. It can also lead to compatibility issues and potentially unstable performance.
Q: How can I check if my computer has a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: You can check for a TPM 2.0 chip by accessing your system’s BIOS settings or using the "tpm.msc" command in the Windows search bar.
Q: What are the benefits of using a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: A TPM 2.0 chip provides enhanced security features, including secure boot, disk encryption, password management, and hardware-based security, significantly reducing the risk of malware attacks and data breaches.
Tips for Users Considering Windows 11:
- Assess your system’s compatibility: Before upgrading to Windows 11, ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements, including the TPM 2.0 chip.
- Check for BIOS updates: Updating your system’s BIOS might enable TPM functionality, even if your motherboard doesn’t have a dedicated chip.
- Explore alternative operating systems: If upgrading to Windows 11 is not feasible, consider alternative operating systems like Linux distributions, which offer robust security and compatibility.
- Prioritize data backup: Before making any significant system changes, ensure you have a reliable backup of your important data to prevent potential data loss.
- Consult with a technical expert: If you’re unsure about the compatibility or security implications of Windows 11, seek advice from a qualified IT professional.
Conclusion
The TPM requirement in Windows 11 represents a significant step towards enhancing system security and protecting user data. While the requirement might present challenges for users with older hardware, it ultimately aims to create a more secure and reliable computing environment. Users should carefully consider their specific needs and security requirements before upgrading to Windows 11 and explore available workarounds or alternative operating systems if necessary. By understanding the importance of security and exploring the available options, users can make informed decisions about their computing environment and ensure a secure and enjoyable experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11: The TPM Requirement and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
