Navigating Windows 11 Without Secure Boot: Understanding the Risks and Alternatives
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Without Secure Boot: Understanding the Risks and Alternatives
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Without Secure Boot: Understanding the Risks and Alternatives. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Without Secure Boot: Understanding the Risks and Alternatives
![[Tutorial] How to Install Windows 11 without Secure Boot and TPM](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/others/others/install-windows-11-without-secure-boot.png)
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, boasts numerous advancements in security and performance. A cornerstone of this enhanced security is Secure Boot, a crucial feature designed to prevent malicious software from loading during the boot process. However, certain scenarios might necessitate running Windows 11 without Secure Boot enabled. This article delves into the implications of disabling this security measure, exploring the potential risks, alternative solutions, and considerations for making informed decisions.
Understanding Secure Boot and Its Importance
Secure Boot is a firmware-level security mechanism that verifies the authenticity of the operating system and other boot components before they are loaded. It essentially acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only trusted software, certified by Microsoft and other reputable entities, can access and control the system. This robust security layer effectively mitigates the threat of malware, rootkits, and other malicious programs from gaining control of the system at its most vulnerable stage – the boot process.
When Disabling Secure Boot Might Be Necessary
While Secure Boot is a crucial security feature, there are scenarios where disabling it might be unavoidable:
- Legacy Hardware Compatibility: Older hardware, particularly motherboards and BIOS/UEFI firmware, might not support Secure Boot. In such cases, disabling Secure Boot allows for the installation and operation of Windows 11 on these systems.
- Specialized Software or Drivers: Certain specialized software or drivers might not be compatible with Secure Boot. This incompatibility could arise from the software’s age, its development environment, or its reliance on specific system functionalities that are restricted by Secure Boot.
- Troubleshooting and Debugging: In specific troubleshooting scenarios, disabling Secure Boot can be beneficial for isolating issues related to the boot process. This allows for a more granular analysis of the boot sequence and identification of potential conflicts or errors.
- Custom Boot Environments: Users with specialized needs, such as developers or system administrators, might require custom boot environments that cannot be achieved with Secure Boot enabled. This includes scenarios where specific boot loaders or kernel modifications are necessary.
The Risks Associated with Disabling Secure Boot
While disabling Secure Boot might seem like a convenient solution in specific situations, it significantly compromises system security. The potential risks associated with running Windows 11 without Secure Boot include:
- Increased Vulnerability to Malware: Without Secure Boot’s verification process, malicious software can potentially gain control of the system during the boot process, bypassing standard security measures. This allows attackers to install malware, steal sensitive data, or take control of the system.
- Compromised System Integrity: Disabling Secure Boot weakens the system’s integrity by allowing unauthorized software and drivers to load. This can lead to instability, crashes, or even permanent damage to the system.
- Difficult Recovery: If a malicious program manages to infect the system without Secure Boot, recovering from the infection can be significantly more challenging. The malicious program might have gained deep-level access to the system, making traditional antivirus solutions less effective.
Alternative Solutions to Consider
Instead of disabling Secure Boot altogether, consider these alternatives to address specific needs while maintaining a secure system:
- Upgrade Hardware: If the issue stems from legacy hardware, upgrading to newer components with Secure Boot support is the most secure solution. This provides a long-term safeguard against vulnerabilities.
- Contact Software Developers: If incompatibility issues arise with specific software or drivers, contact the developer for updates or alternative solutions that are compatible with Secure Boot.
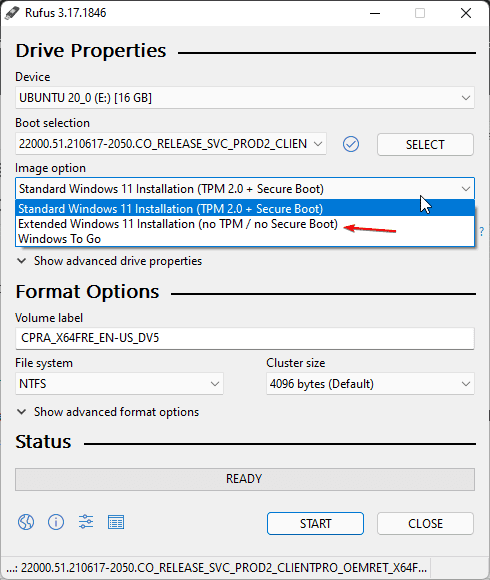
- Utilize Virtual Machines: For testing or development purposes, consider using virtual machines. Virtualization allows for the creation of isolated environments where Secure Boot can be disabled without compromising the host system’s security.
- Explore Secure Boot Customization: Some motherboards and BIOS/UEFI firmware offer advanced Secure Boot customization options. Explore these settings to see if they allow for specific configurations that address your needs while maintaining a secure environment.
FAQs Regarding Windows 11 Without Secure Boot
Q: Is it safe to run Windows 11 without Secure Boot?
A: No, running Windows 11 without Secure Boot significantly compromises system security, increasing vulnerability to malware and other threats. It is strongly recommended to enable Secure Boot whenever possible.
Q: What are the consequences of disabling Secure Boot?
A: Disabling Secure Boot weakens the system’s defenses, allowing malicious programs to load during the boot process. This can lead to system instability, data breaches, and difficulty in recovering from infections.
Q: Can I disable Secure Boot temporarily for troubleshooting?
A: While disabling Secure Boot for troubleshooting might be necessary in specific scenarios, it is crucial to re-enable it as soon as the issue is resolved. Prolonged use without Secure Boot exposes the system to significant security risks.
Q: What are the best practices for running Windows 11 without Secure Boot?
A: If disabling Secure Boot is unavoidable, consider these best practices to mitigate risks:
- Use a trusted antivirus solution: Ensure that a comprehensive antivirus program is installed and updated regularly to detect and remove malware.
- Be cautious with software downloads: Only download software from reputable sources and avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Keep the system updated: Regularly install the latest Windows updates and security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication: Protect user accounts with strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
Tips for Managing Secure Boot in Windows 11
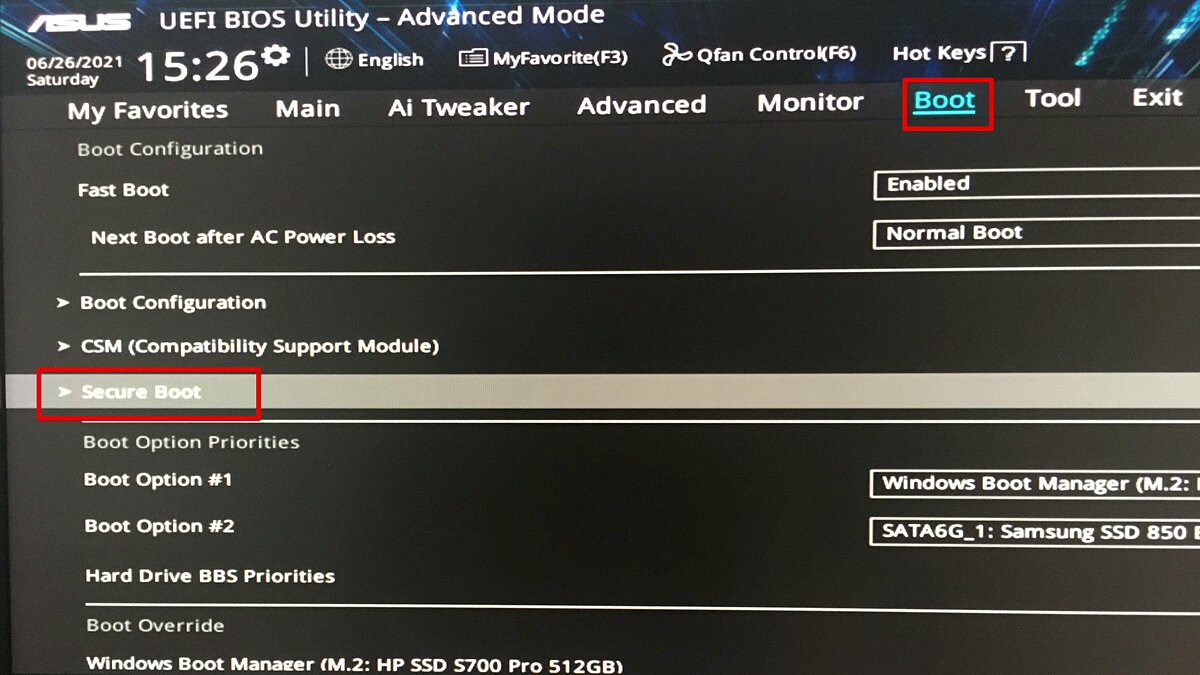
- Verify Secure Boot Status: Access the BIOS/UEFI settings and check the Secure Boot status. Ensure it is enabled for optimal security.
- Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware: Regularly check for updates to the motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI firmware. Updates often include security enhancements and bug fixes.
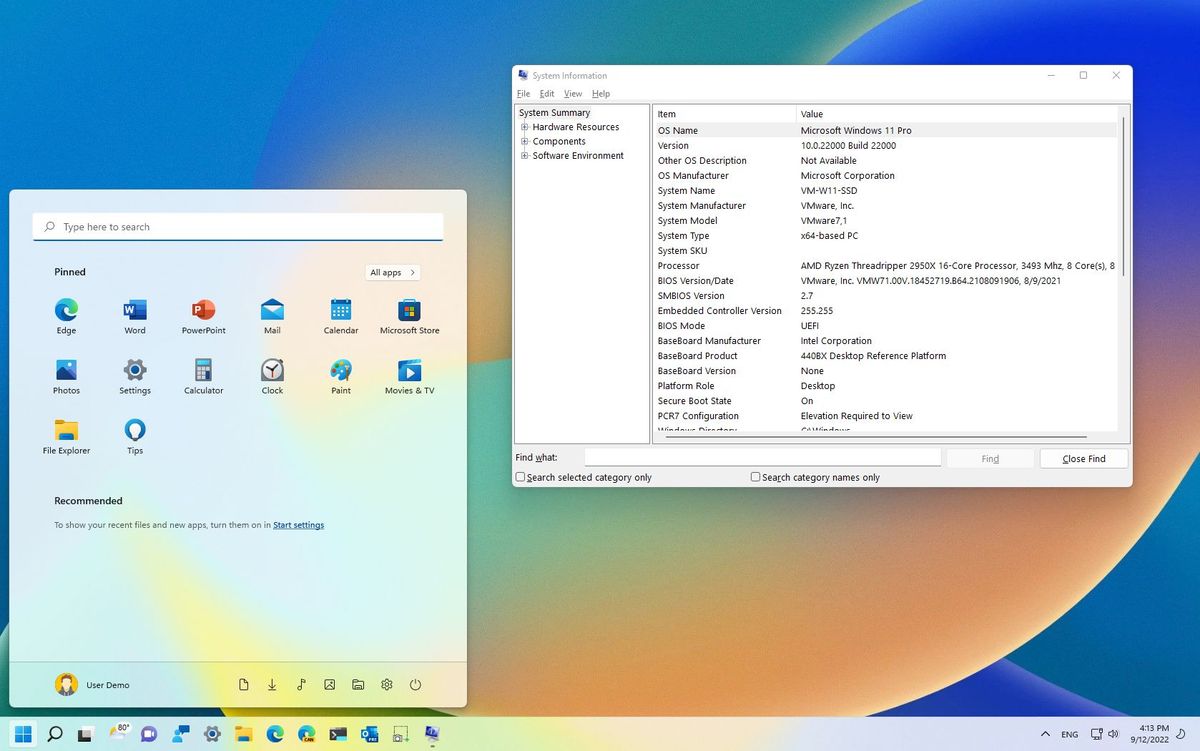
- Consider Trusted Platform Module (TPM): A TPM is a hardware security module that works in conjunction with Secure Boot to further enhance system security.
Conclusion
While disabling Secure Boot might be necessary in specific situations, it is a decision that should not be taken lightly. The potential security risks associated with running Windows 11 without Secure Boot are substantial. By understanding the implications and considering alternative solutions, users can make informed decisions that prioritize security while addressing specific needs. Always prioritize enabling Secure Boot whenever possible to ensure a secure and reliable computing experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Without Secure Boot: Understanding the Risks and Alternatives. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
