Troubleshooting Windows 11 Startup Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Startup Issues: When Safe Mode Fails
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 11 Startup Issues: When Safe Mode Fails. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 11 Startup Issues: When Safe Mode Fails

The inability to boot into Safe Mode on Windows 11 can be a frustrating and potentially debilitating issue for users. Safe Mode is a crucial troubleshooting tool, allowing users to diagnose and resolve problems that prevent the operating system from starting normally. This mode loads only essential drivers and services, eliminating potential conflicts and allowing for targeted problem resolution. When Safe Mode fails to initiate, it signals a deeper underlying issue that requires a systematic and methodical approach to resolve.
Understanding the Importance of Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a diagnostic environment that isolates the operating system from potentially problematic software and hardware. It operates with a minimal set of drivers and services, providing a clean slate for troubleshooting. This mode is invaluable for diagnosing and resolving issues like:
- Driver Conflicts: Faulty or incompatible drivers can cause system instability and prevent Windows from starting properly. Safe Mode allows users to disable or update problematic drivers without the interference of other applications.
- Malware Infections: Some malware can interfere with the normal boot process or hide within system files. Safe Mode provides a secure environment to run antivirus scans and remove malicious software.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or corrupted software can cause system errors and prevent Windows from booting. Safe Mode enables users to uninstall problematic applications or repair corrupted files.
- Hardware Issues: Faulty hardware components, such as a failing hard drive or RAM module, can disrupt the boot process. Safe Mode can help identify hardware malfunctions by isolating the operating system from potential conflicts.
Common Causes of Safe Mode Failure
The inability to boot into Safe Mode can stem from various factors, each requiring a different approach to resolution. Some common causes include:
- Corrupted Boot Files: Essential system files, such as the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) or Windows Registry, can become corrupted due to software errors, malware infections, or power outages.
- Faulty Drivers: Incompatible or outdated drivers can prevent the system from loading necessary components for Safe Mode.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Damaged or faulty hardware, such as the hard drive or RAM, can disrupt the boot process and hinder access to Safe Mode.
- Malware Interference: Certain malware can actively block access to Safe Mode to prevent detection and removal.
- System Configuration Issues: Incorrect settings in the Windows Boot Manager or BIOS can prevent the system from booting into Safe Mode.
Troubleshooting Steps: A Systematic Approach
Resolving Safe Mode failure requires a structured approach to identify and address the root cause. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting:
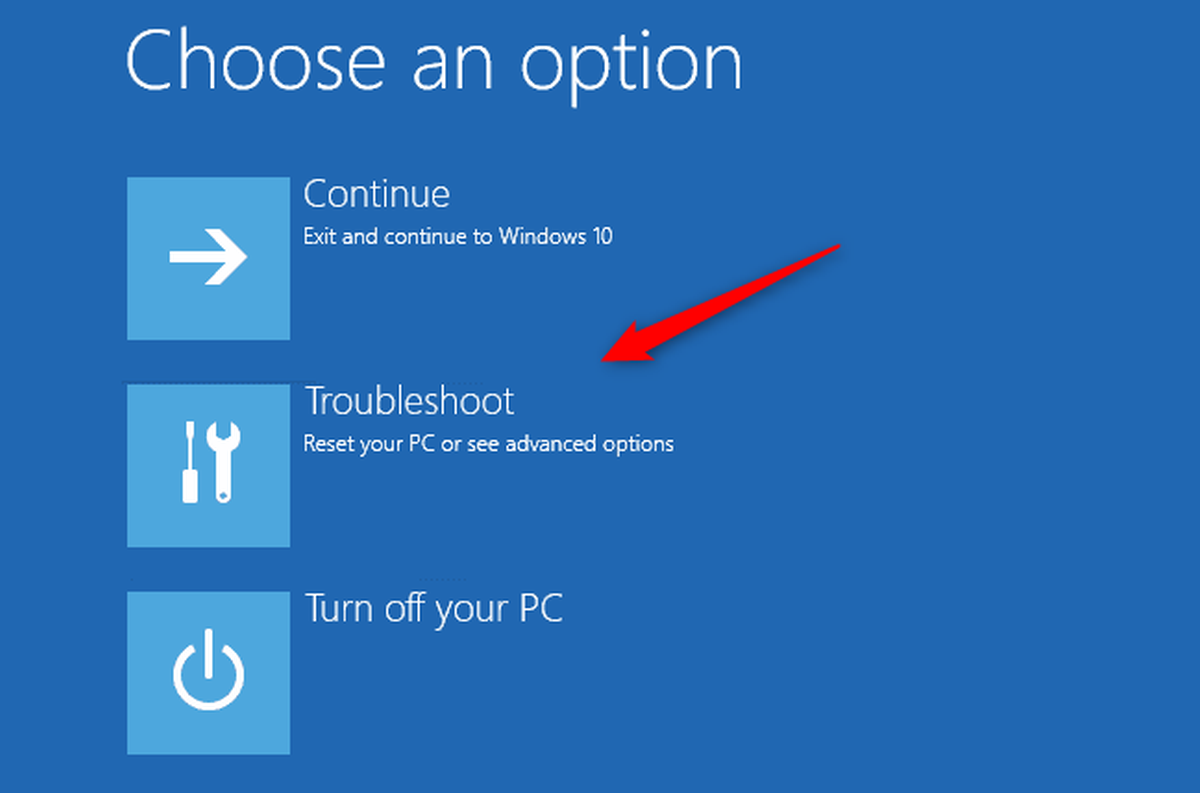
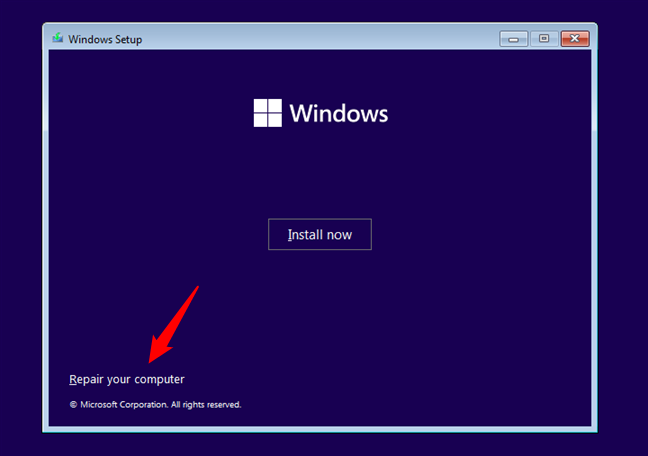
1. Accessing the Advanced Startup Options:
- Restart the Computer: Press and hold the power button to force a shutdown, then restart the computer.
- Access Boot Options: During startup, repeatedly press the F2, F8, F10, or Del key (the specific key depends on the motherboard manufacturer) to enter the BIOS or UEFI settings.
- Select Boot Options: Navigate to the Boot menu and select "Advanced Startup Options" or a similar option.
2. Utilizing System Recovery Options:
- Startup Repair: This tool attempts to automatically detect and repair boot-related issues, including corrupted system files.
- System Restore: Reverts the system to a previous restore point, potentially restoring functionality and allowing access to Safe Mode.
- Command Prompt: Provides a command-line interface for advanced troubleshooting, allowing users to manually repair boot files or perform other system-level operations.
3. Checking for Hardware Issues:
- RAM Testing: Utilize a memory testing tool, like Memtest86+, to identify and isolate faulty RAM modules.
- Hard Drive Check: Run a hard drive diagnostic tool, such as the built-in Windows Check Disk (chkdsk) utility, to identify and potentially repair errors.
4. Addressing Driver Conflicts:
- Driver Rollback: If a recent driver update caused Safe Mode failure, consider rolling back to a previous version of the driver.
- Driver Update: In some cases, updating to the latest driver version can resolve compatibility issues and enable Safe Mode.
- Disabling Drivers: Temporarily disable problematic drivers in Safe Mode (if accessible) to isolate and identify the culprit.
5. Removing Malware:
- Boot-Time Scan: If possible, run an antivirus scan from a bootable USB drive or CD to detect and remove malware that might be interfering with Safe Mode.
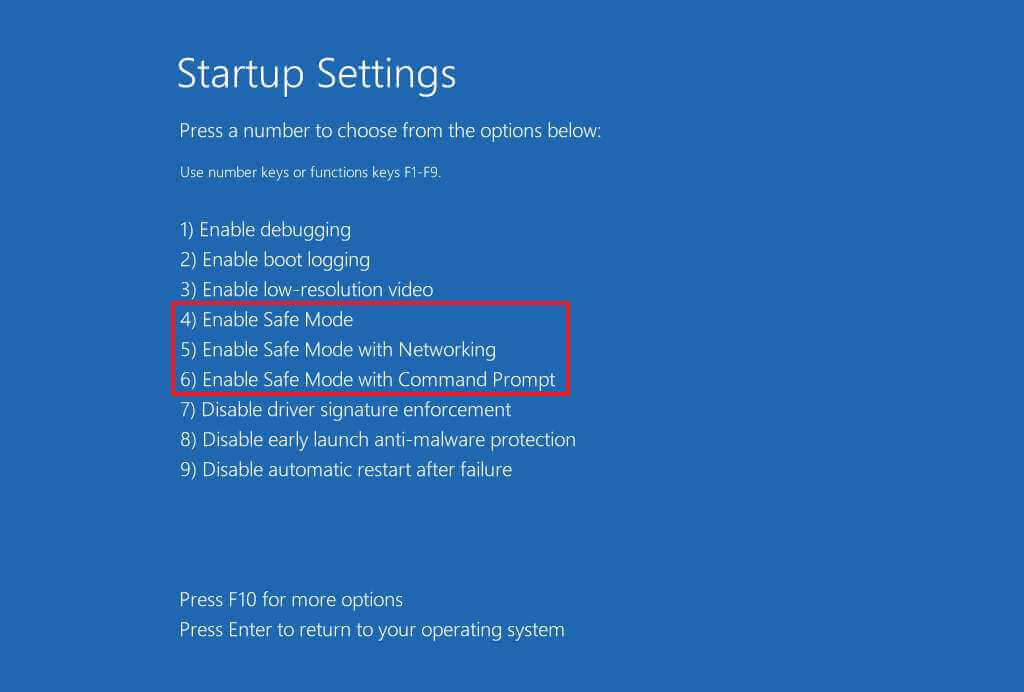
- Safe Mode (if Accessible): If Safe Mode is accessible, run a full system scan with your antivirus software.
6. Modifying System Configuration:
- Boot Configuration Data (BCD): Use the "bcdedit" command in the Command Prompt to modify boot settings and potentially resolve Safe Mode issues.
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: Check for any boot-related settings in the BIOS or UEFI that might be preventing Safe Mode from loading.
7. Seeking Professional Assistance:
If the troubleshooting steps above fail to resolve the Safe Mode issue, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician or computer repair service.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What if I cannot access Safe Mode at all?
A: If Safe Mode is inaccessible, consider utilizing a bootable USB drive or CD with a live operating system, such as Ubuntu or Linux Mint. These operating systems provide a temporary environment to access files and troubleshoot issues.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode to repair a corrupted Windows installation?
A: While Safe Mode can be helpful for troubleshooting certain issues, it might not be sufficient to repair a severely corrupted Windows installation. In such cases, a clean installation might be necessary.
Q: Is it safe to modify boot settings using the Command Prompt?
A: Modifying boot settings through the Command Prompt requires caution. Incorrect commands can lead to system instability or data loss. It is advisable to consult with a qualified technician or refer to reliable online resources before attempting any modifications.
Tips for Preventing Safe Mode Failure
- Regularly Update Drivers: Ensure that all device drivers are up to date to prevent compatibility issues and ensure system stability.
- Run Antivirus Scans: Regularly scan your system for malware to prevent infections that can disrupt the boot process.
- Create System Restore Points: Regularly create system restore points to provide a fallback option if system issues arise.
- Back Up Important Data: Regularly back up important files and data to protect against data loss in case of system failures.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Resolution
The inability to boot into Safe Mode on Windows 11 can be a challenging problem, but with a systematic and methodical approach, it is often resolvable. By understanding the common causes, applying the appropriate troubleshooting steps, and seeking professional assistance when necessary, users can overcome this obstacle and restore their system’s functionality. Remember, maintaining a clean and updated system, running regular antivirus scans, and creating system restore points can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering such issues in the future.

![How to Boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode [Easy Guide]](https://www.stellarinfo.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Advanced-options-startup-settings_image-3.jpg)
![Fix Common Startup Problems In Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dodsRVyqcoU/maxresdefault.jpg)

![Windows 11 Startup Repair Not Working? 4 BEST FIX [2021]](https://www.thecpuguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/startup-repair-windows-11.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 11 Startup Issues: When Safe Mode Fails. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
