Understanding the Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Malware in the Windows 11 Ecosystem
Related Articles: Understanding the Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Malware in the Windows 11 Ecosystem
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Malware in the Windows 11 Ecosystem. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Malware in the Windows 11 Ecosystem
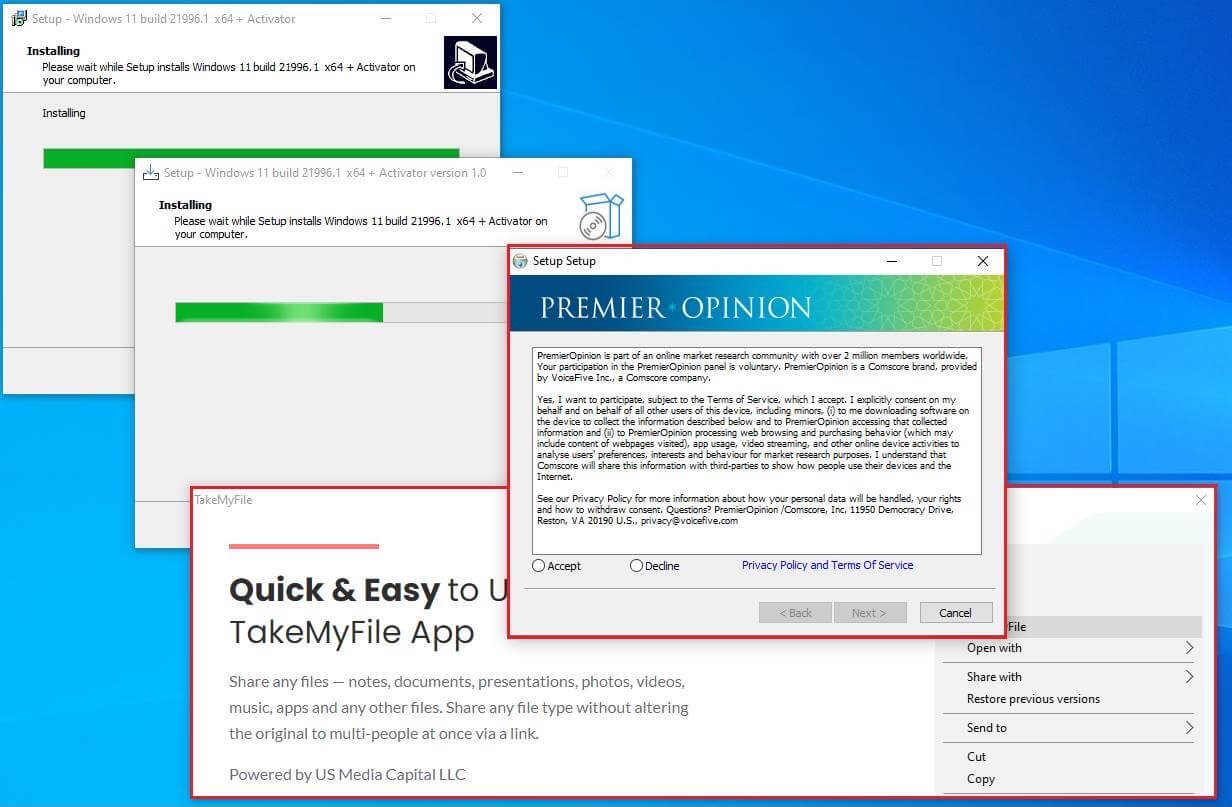
The advent of Windows 11 brought with it a renewed focus on security, promising enhanced protection against malicious software. However, the reality is that the threat of malware remains a persistent concern, evolving alongside the operating system itself. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape of malware targeting Windows 11, examining its various forms, methods of infection, and the best practices for mitigation.
The Evolving Landscape of Malware:
Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a wide range of programs designed to infiltrate and compromise computer systems. These programs can range from simple annoyances to highly sophisticated threats capable of stealing sensitive data, disrupting system functionality, or even gaining control of the infected device.
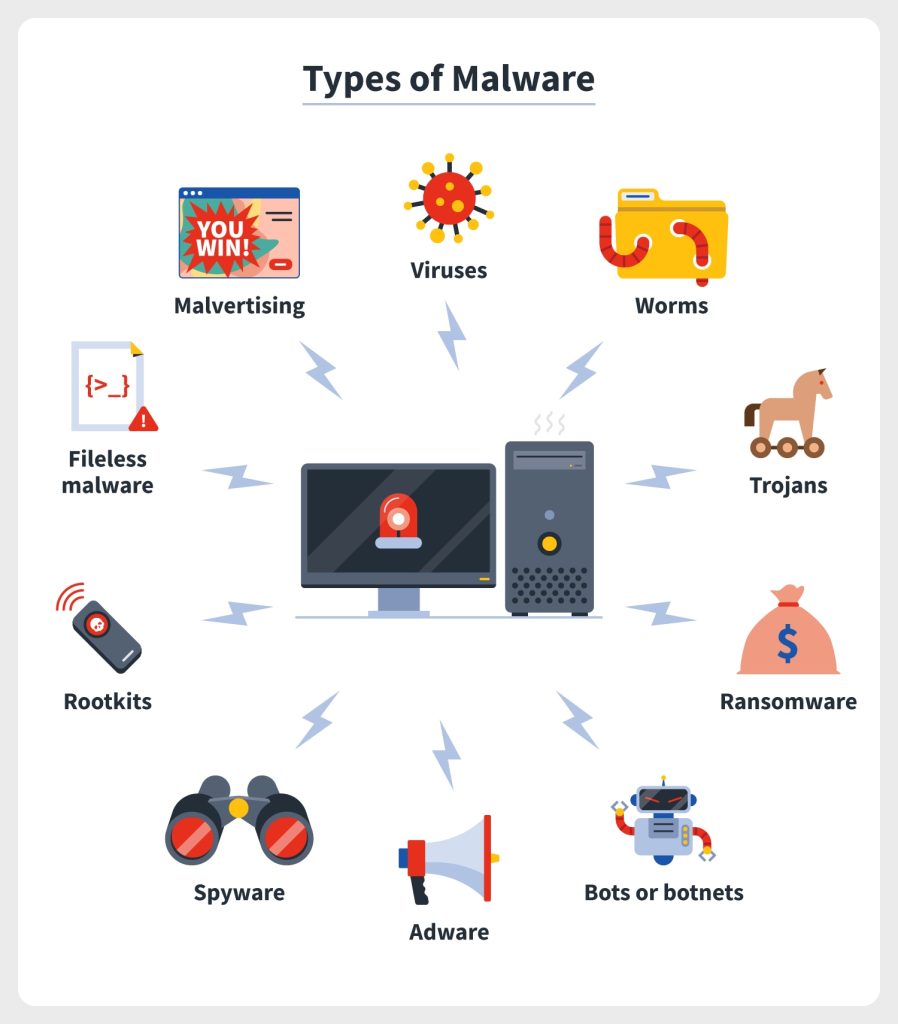
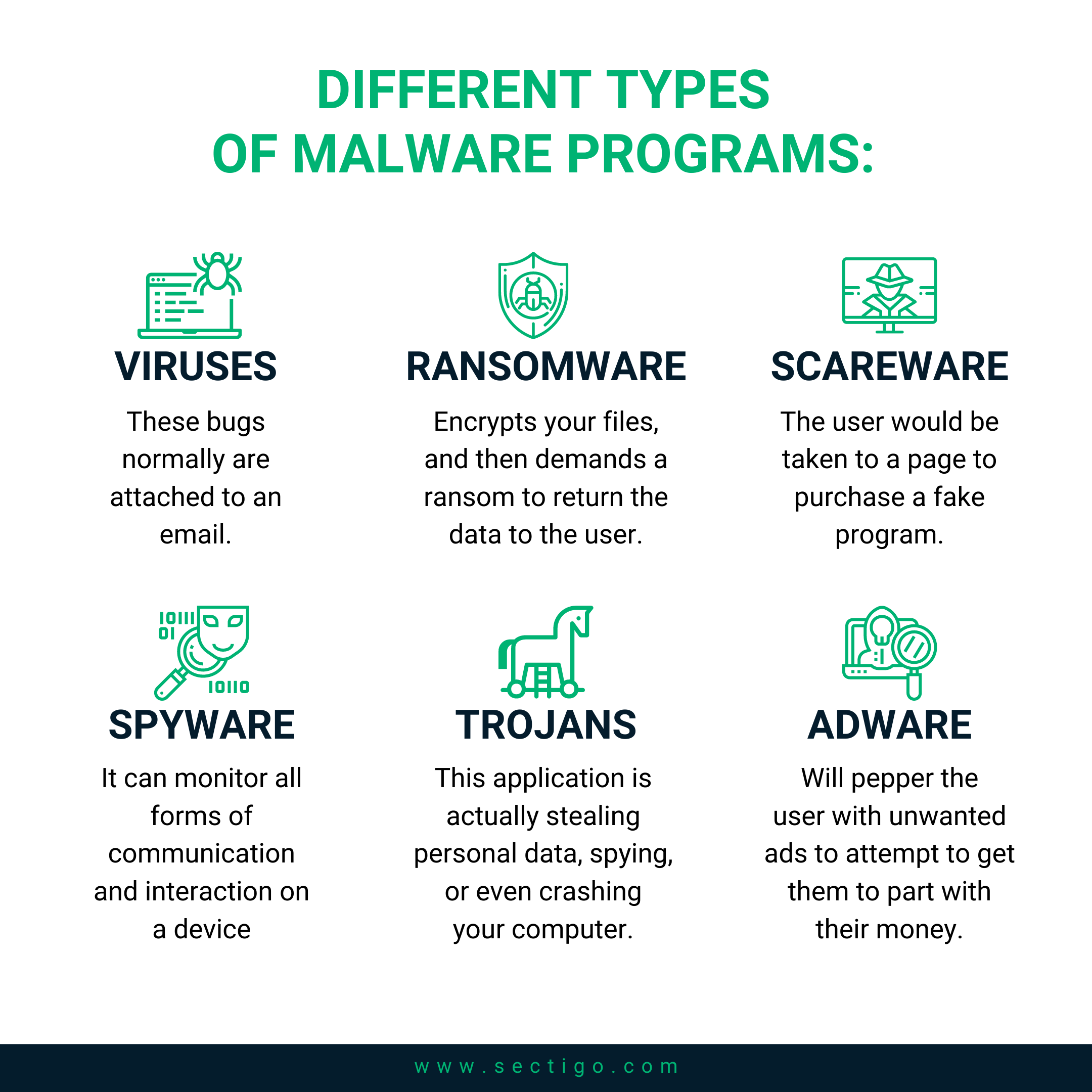
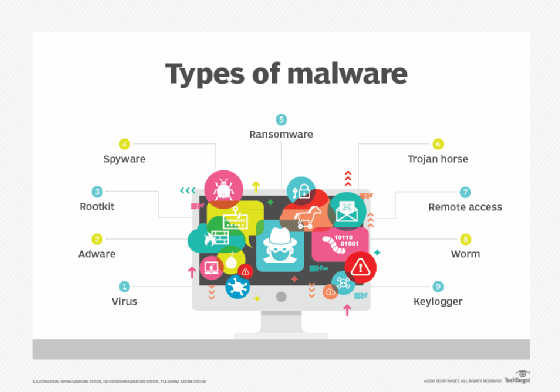
In the context of Windows 11, malware can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Viruses: These are self-replicating programs that spread by attaching themselves to other executable files. They can cause a range of problems, from data corruption to system crashes.
- Worms: These are self-propagating malware that can spread without human intervention, often exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols or software applications.
- Trojan Horses: These programs masquerade as legitimate software but contain hidden malicious code. Once installed, they can steal information, provide remote access to the infected device, or install additional malware.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts a user’s files and demands payment for their decryption.
- Spyware: These programs collect personal information without the user’s knowledge or consent, often transmitting this data to third parties.
- Adware: This malware displays unwanted advertisements on the user’s computer, often redirecting them to malicious websites.
Methods of Infection:
Malware can spread through various methods, including:
- Malicious Websites: Visiting compromised websites can expose users to drive-by downloads, where malware is automatically installed without the user’s consent.
- Email Attachments: Opening malicious attachments in emails can lead to malware infection.
- File Sharing Networks: Downloading files from untrusted sources, such as peer-to-peer networks, can expose users to malware.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Exploiting security vulnerabilities in software can allow malware to gain access to the system.
- USB Drives: Connecting infected USB drives can lead to malware infection.
Recognizing the Signs of Infection:
Identifying malware infection early is crucial for mitigating damage and preventing further spread. Common signs of infection include:
- Slow System Performance: Malware can consume system resources, leading to sluggish performance and frequent crashes.
- Unexplained Programs: The presence of unfamiliar programs or processes can indicate malware infection.
- Pop-up Advertisements: Excessive or intrusive pop-up advertisements can be a sign of adware infection.
- Unusual Network Activity: Increased network usage or unusual traffic patterns can indicate malware communicating with remote servers.
- Data Loss or Corruption: Malware can corrupt or delete data files.
- Changes in System Settings: Malware can modify system settings, such as browser settings or firewall configurations.
Protecting Your Windows 11 System:
Protecting your Windows 11 system from malware requires a multi-layered approach:
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, software applications, and drivers to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use a Comprehensive Antivirus Program: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus program that provides real-time protection against malware threats.
- Be Cautious with Email Attachments: Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or those that seem suspicious.
- Be Wary of Websites: Avoid visiting websites that appear untrustworthy or that offer free software downloads.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for your accounts and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
- Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your important data to an external drive or cloud storage service.
- Enable Windows Defender: Windows 11 includes built-in antivirus protection known as Windows Defender. Ensure it is enabled and regularly updated.
- Be Vigilant: Stay informed about the latest malware threats and be cautious about clicking on links or downloading files from unknown sources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Is Windows 11 more vulnerable to malware than previous versions of Windows?
A: While Windows 11 includes enhanced security features, it is not inherently more vulnerable than previous versions. However, new operating systems often become targets for malware developers who seek to exploit vulnerabilities in the system or newly released applications.
Q: How do I know if my computer is infected with malware?
A: Look for signs of infection, such as slow performance, unexplained programs, unusual network activity, or changes in system settings. Running a full system scan with your antivirus software can also help detect malware.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my computer is infected with malware?
A: Disconnect from the internet, run a full system scan with your antivirus software, and consider using a dedicated malware removal tool. If you are unable to remove the malware yourself, contact a professional cybersecurity expert.
Q: Can I remove malware without using antivirus software?
A: While some malware can be removed manually, it is generally recommended to use antivirus software for comprehensive protection and removal.
Q: What are the best ways to prevent malware infection?
A: Follow the tips mentioned earlier, including keeping your software updated, using a comprehensive antivirus program, being cautious with email attachments and websites, and using strong passwords.
Tips for Staying Safe:
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest malware threats and learn how to identify and avoid them.
- Practice Safe Browsing: Avoid visiting websites that appear untrustworthy or that offer free software downloads.
- Be Cautious with Social Media: Be wary of links and attachments shared on social media platforms, especially those from unknown sources.
- Use a Password Manager: A password manager can help you create and store strong passwords for your accounts.
- Be Aware of Phishing Scams: Be cautious of emails or messages that ask for personal information or that try to trick you into clicking on malicious links.
Conclusion:
Malware remains a significant threat to Windows 11 users, but with proper awareness and proactive measures, it is possible to minimize the risks. By staying informed, implementing security best practices, and using reputable antivirus software, users can significantly reduce their vulnerability to malware and protect their systems from harm. Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and vigilance is key to staying safe in the evolving digital landscape.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Malware in the Windows 11 Ecosystem. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
