Unlocking the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Virtual Machines
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Virtual Machines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Virtual Machines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Virtual Machines
Virtualization, a technology that allows running multiple operating systems concurrently on a single physical machine, has become an indispensable tool for developers, IT professionals, and even everyday users. Among the most popular operating systems for virtualization, Windows 11 stands out with its advanced features and user-friendly interface. This article delves into the intricacies of creating a Windows 11 virtual machine, exploring its benefits, and providing a comprehensive guide to navigating the process.
Understanding Virtualization and its Significance
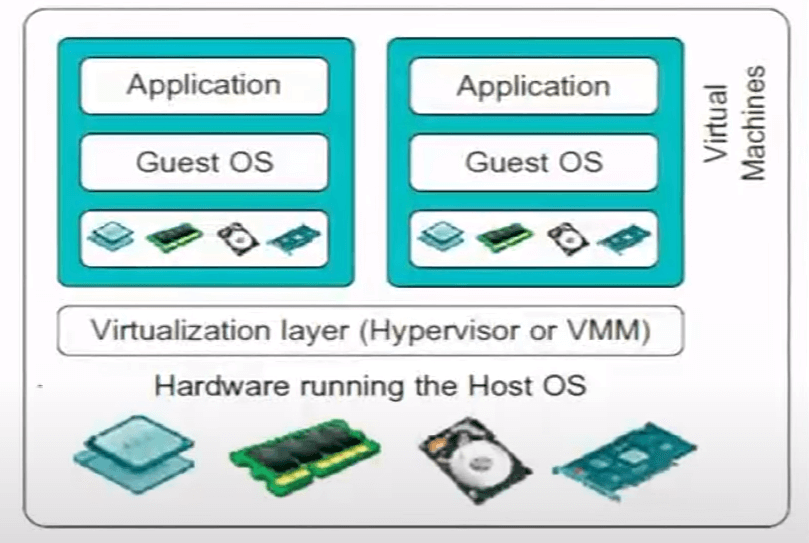
Virtualization fundamentally involves creating a simulated environment, a virtual machine (VM), within a host operating system. This virtual machine functions as an independent computer, capable of running its own operating system, applications, and data, isolated from the host system.
The significance of virtualization lies in its ability to:
- Test and Develop Software: Developers can create multiple virtual environments to test their applications across various operating systems and configurations without impacting the host system.
- Run Legacy Applications: Virtualization allows users to run older applications that may not be compatible with newer operating systems.
- Improve System Security: By isolating sensitive applications and data within a virtual machine, users can enhance system security and limit the impact of potential security breaches.
- Optimize Resource Utilization: Virtualization enables users to consolidate multiple physical machines into fewer, more powerful servers, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Experiment with New Technologies: Virtual machines provide a safe space to explore new operating systems, software, and configurations without affecting the primary operating system.
Choosing the Right Virtualization Software
The first step in creating a Windows 11 virtual machine is selecting the appropriate virtualization software, also known as a hypervisor. There are two primary types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 (Bare-Metal): These hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware, offering high performance and control. Examples include VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Type 2 (Hosted): These hypervisors run within a host operating system, providing a more user-friendly interface and easier setup. Popular examples include Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Player.
The choice between a Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisor depends on specific needs and resources. For users seeking ease of use and affordability, hosted hypervisors are a suitable option. However, for demanding applications requiring high performance and advanced features, bare-metal hypervisors are the preferred choice.
Creating a Windows 11 Virtual Machine: A Step-by-Step Guide
The process of creating a Windows 11 virtual machine varies depending on the chosen virtualization software. However, the general steps remain consistent:
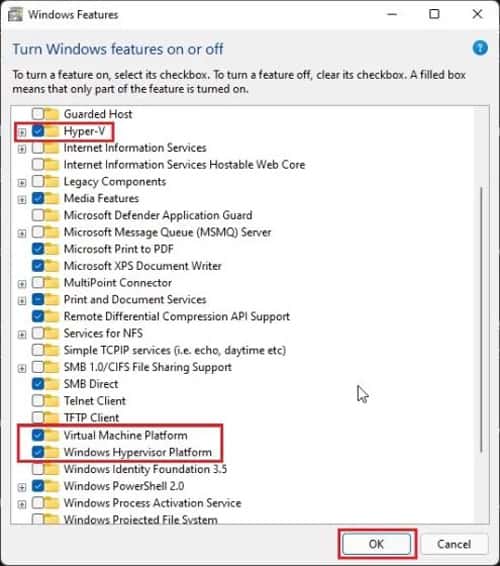
- Install and Configure the Hypervisor: Download and install the chosen virtualization software on the host machine. Configure the hypervisor settings, such as memory allocation, network connections, and storage options.
- Create a New Virtual Machine: Launch the hypervisor and select the option to create a new virtual machine. Specify the virtual machine name, operating system type (Windows 11), and allocate sufficient resources (CPU cores, RAM, and storage).
- Install the Windows 11 Operating System: Choose the desired Windows 11 ISO file and select the appropriate installation method. The installation process will involve formatting the virtual hard drive, configuring the operating system, and creating user accounts.
- Configure Virtual Machine Settings: After the installation is complete, customize the virtual machine settings to optimize performance and functionality. This may include adjusting the network settings, adding additional storage, and configuring the display resolution.
- Install and Configure Software: Once the Windows 11 virtual machine is set up, install the desired applications and software. Remember to update the operating system and all installed applications regularly for optimal performance and security.
Essential Tips for Optimizing Windows 11 Virtual Machines
- Allocate Sufficient Resources: Ensure the virtual machine has enough CPU cores, RAM, and storage space to run smoothly. Consider the requirements of the intended applications and operating system.
- Enable Hardware Acceleration: Enable hardware acceleration within the hypervisor settings to enhance performance. This allows the virtual machine to leverage the host machine’s hardware resources for faster processing.
- Optimize Network Settings: Configure the network settings to provide the virtual machine with adequate bandwidth and connectivity. Consider using a dedicated network adapter or configuring a virtual network for optimal performance.
- Regularly Update the Virtual Machine: Keep the Windows 11 operating system, applications, and hypervisor software up-to-date with the latest patches and security updates.
- Back Up Virtual Machine Data: Regularly back up the virtual machine data to prevent data loss in case of hardware failure or system corruption.
Frequently Asked Questions about Windows 11 Virtual Machines
Q: What are the system requirements for running a Windows 11 virtual machine?
A: The system requirements for running a Windows 11 virtual machine depend on the chosen hypervisor and the intended usage. However, as a general guideline, the host system should have at least 4 GB of RAM, a dual-core processor, and a minimum of 20 GB of free hard disk space.
Q: Can I use my existing Windows 11 license to activate a virtual machine?
A: Microsoft’s licensing terms generally allow users to install Windows on a virtual machine using the same license key as the host operating system. However, it is essential to consult Microsoft’s licensing guidelines for specific details and limitations.
Q: How can I improve the performance of my Windows 11 virtual machine?
A: You can improve the performance of a Windows 11 virtual machine by allocating more resources (CPU cores, RAM, storage), enabling hardware acceleration, optimizing network settings, and updating the virtual machine and hypervisor software regularly.
Q: Are there any security risks associated with running a Windows 11 virtual machine?
A: Virtual machines, like any other software, can be vulnerable to security threats. It is crucial to keep the virtual machine, hypervisor, and all installed applications up-to-date with the latest security patches. Additionally, consider using strong passwords and enabling security features within the virtual machine, such as antivirus software and firewalls.
Conclusion
Virtual machines offer a powerful and versatile platform for various purposes, from software development and testing to running legacy applications and experimenting with new technologies. Windows 11, with its advanced features and user-friendly interface, has become a popular choice for creating virtual machines. By understanding the principles of virtualization, choosing the right hypervisor, and following the steps outlined in this guide, users can leverage the full potential of Windows 11 virtual machines. Remember to prioritize security, performance, and regular updates to ensure a smooth and reliable virtual machine experience.


![Enable Virtualization in Windows 11 [GUIDE] - Thetecheaven](https://thetecheaven.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Enable-Virtualization-in-Windows-11.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Virtual Machines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
