Unraveling the Mystery of Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery of Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery of Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11

Windows 11, with its sleek interface and enhanced performance, promises a seamless computing experience. However, some users encounter an unexpected hurdle: a sluggish startup after the system awakens from sleep mode. This phenomenon, while frustrating, is not inherently a sign of a faulty system. Instead, it often stems from a combination of factors that can be addressed through troubleshooting and optimization.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Sleep Mode:
To comprehend the root of the issue, it is crucial to understand how Windows 11 handles sleep mode. When a system enters sleep mode, it enters a low-power state, preserving the current system state in RAM. This allows for quick resumption, effectively "freezing" the system until the user wakes it up. However, the transition between sleep and wakefulness involves a series of processes, and any hiccups in these processes can lead to prolonged startup times.
Common Culprits Behind Slow Startup After Sleep:
Several factors can contribute to the slow startup issue after sleep mode:
- Outdated or Incompatible Drivers: Drivers, the software that allows hardware components to communicate with the operating system, are critical for smooth operation. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to conflicts and delays, particularly during the wake-up process.
- Background Applications: Numerous applications run silently in the background, often consuming resources even when not actively used. These applications can interfere with the wake-up process, leading to sluggish performance.
- Hardware Issues: In some cases, the culprit might lie within the hardware itself. A failing hard drive or malfunctioning RAM can cause delays during system startup, particularly after sleep.
- System Files Corruption: Over time, system files can become corrupted, leading to errors and inconsistencies that can affect the wake-up process.
- Power Management Settings: Incorrectly configured power management settings can lead to the system entering a deeper sleep state, requiring more time to wake up.
- Third-Party Software Conflicts: Certain third-party software, especially security programs and system optimization tools, can interfere with the normal operation of the system, potentially causing delays during startup.
- System Resource Overutilization: When the system is heavily loaded with running applications or background processes, the wake-up process can be slowed down due to insufficient resources.
Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies:
Addressing slow startup after sleep requires a systematic approach:
- Update Drivers: Regularly updating drivers to the latest versions ensures compatibility and optimal performance. Use the Windows Update feature or visit the manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers.
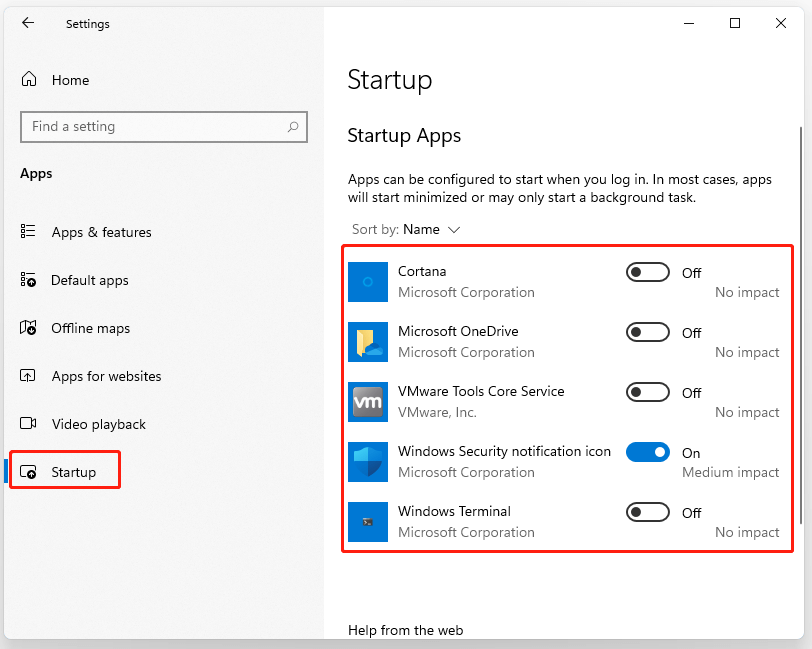
- Manage Background Applications: Identify and disable unnecessary background applications that consume resources. Use the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to identify resource-intensive processes and disable them.
- Run System File Checker: The System File Checker (SFC) tool can scan for and repair corrupted system files. Run the command "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt (Admin) to initiate the scan.
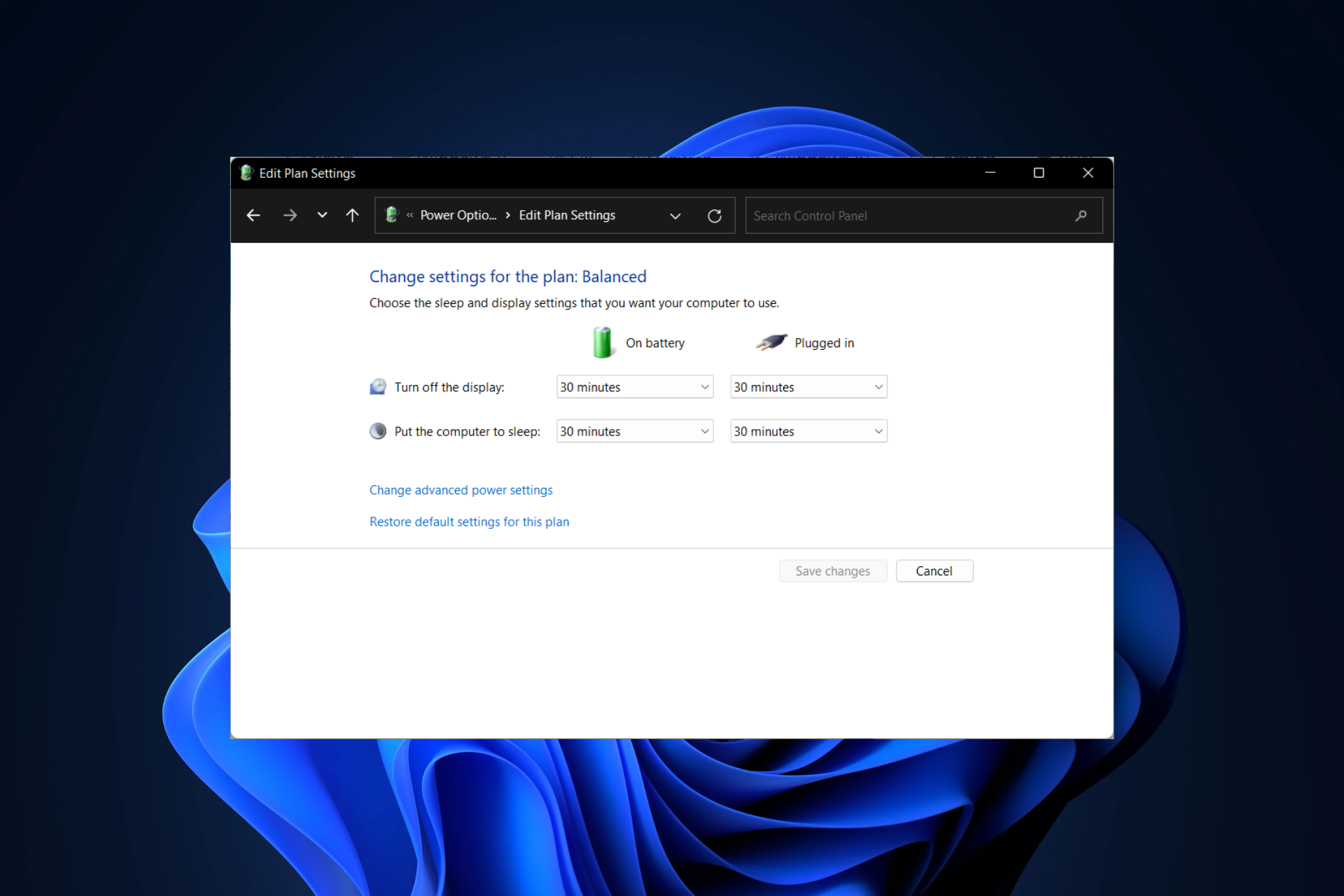
- Optimize Power Settings: Configure power management settings to ensure the system enters a balanced sleep state that allows for quick wake-up. Access power settings through the Control Panel or search for "power options" in the Windows search bar.
- Check for Hardware Issues: Run diagnostic tests on hardware components like RAM and hard drives to rule out any potential hardware failures.
- Disable Fast Startup: While Fast Startup can speed up system boot, it can sometimes lead to delays after sleep. Disable Fast Startup in the Power Options settings.
- Perform a Clean Boot: Starting the system in a clean boot state eliminates the influence of third-party software, allowing you to identify if any specific application is causing the issue.
- Reinstall Windows: As a last resort, reinstalling Windows can resolve deep-seated issues that may be causing the slow startup problem. However, this should be considered only after exhausting other troubleshooting options.
FAQs Regarding Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11:
Q: Why does my laptop take longer to start after sleep than after a full shutdown?
A: Sleep mode aims for quicker resumption than a full shutdown. However, certain processes, like driver loading, might still be required during wake-up, contributing to a slightly longer startup time compared to a fresh boot.
Q: Is it normal for my computer to be slow after waking from sleep?
A: A slight delay is expected, but excessive slowness indicates an underlying issue. Factors like outdated drivers, background processes, or hardware problems can contribute to prolonged startup times.
Q: How do I know if a driver is causing the slow startup?
A: Observe if the slow startup occurs after installing a new driver or updating an existing one. Roll back the driver or update to a different version to see if it resolves the issue.
Q: What are some common background applications that might be slowing down my computer?
A: Common culprits include antivirus software, cloud synchronization services, and system monitoring tools. Identify these applications in the Task Manager and disable them temporarily to see if it improves startup times.
Q: Is it safe to disable Fast Startup?
A: Disabling Fast Startup is generally safe and can improve performance in certain situations. However, it might slightly increase boot times.
Q: What should I do if I suspect a hardware issue is causing the slow startup?
A: Run diagnostic tests on the hard drive and RAM to check for errors. If any issues are detected, consider replacing the affected component.
Tips for Optimizing Startup After Sleep:
- Minimize Startup Programs: Reduce the number of programs that automatically launch at startup. This can be done through the Task Manager or the System Configuration utility.
- Utilize Disk Cleanup: Regularly run the Disk Cleanup tool to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space, potentially improving performance.
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: For traditional hard drives, defragmentation can improve performance by organizing data more efficiently.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly check the Task Manager for resource-intensive processes and consider closing or adjusting their settings.
- Maintain System Updates: Ensure Windows is up to date with the latest security patches and updates, as these often include performance improvements.
Conclusion:
While slow startup after sleep in Windows 11 can be frustrating, it is often a solvable problem. By understanding the potential causes and employing the troubleshooting and optimization strategies outlined, users can effectively address this issue and regain a smooth and responsive computing experience. It is important to approach the issue systematically, starting with basic troubleshooting steps and gradually moving towards more advanced solutions if necessary. By taking proactive steps to manage system resources, update drivers, and maintain a clean system environment, users can minimize the likelihood of encountering slow startup issues and enjoy a seamless Windows 11 experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery of Slow Startup After Sleep in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
