Unraveling the Mystery: Why is Hibernate Disabled in Windows 11?
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery: Why is Hibernate Disabled in Windows 11?
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery: Why is Hibernate Disabled in Windows 11?. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery: Why is Hibernate Disabled in Windows 11?
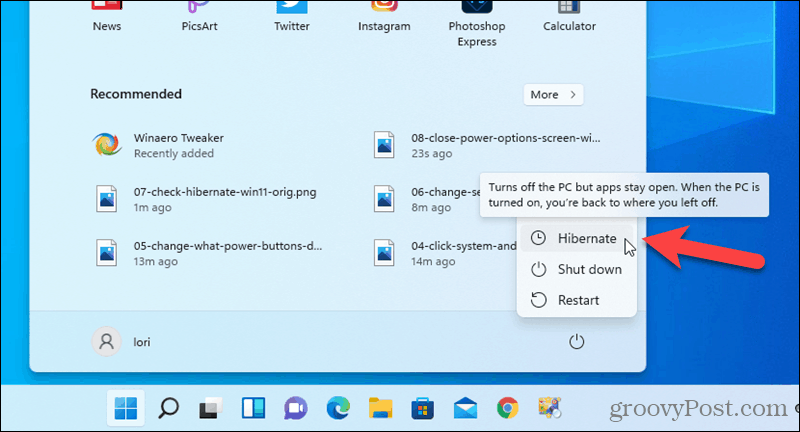
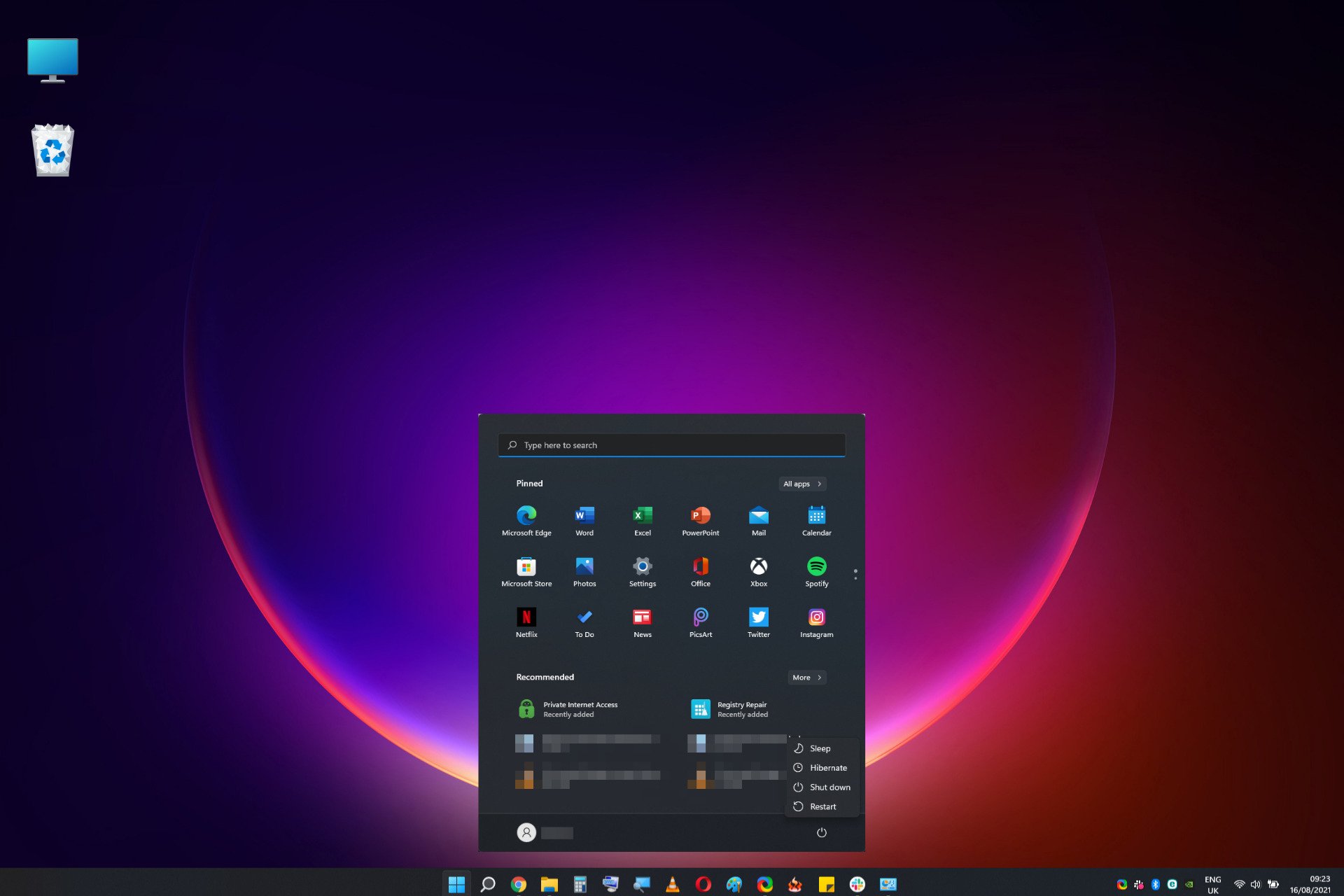
The "Hibernate" option, once a familiar feature in Windows, may be absent in Windows 11 for a variety of reasons. This absence, while seemingly inconvenient, often stems from a deliberate design choice aimed at optimizing user experience and system performance. Understanding the factors contributing to this change and the potential benefits it brings is crucial for navigating the landscape of Windows 11.
Understanding the Mechanics of Hibernate
Before delving into the reasons behind the disabled hibernate option, it’s essential to understand the core functionality of this feature. Hibernate, in essence, is a power-saving mode that allows a computer to enter a state of deep sleep. Unlike sleep mode, which keeps the computer in a low-power state while retaining data in RAM, hibernate saves the current state of the operating system and all open applications to the hard drive. This ensures a faster boot-up time than a cold start, as the system can resume its previous state directly from the hard drive.
The Evolving Landscape of Windows 11
Windows 11, with its emphasis on efficiency and modern user experience, has undergone significant changes from its predecessors. These changes, while generally beneficial, can sometimes lead to the absence of certain features, including hibernate.
Factors Contributing to the Absence of Hibernate:
1. Fast Startup: Windows 11 leverages a feature called "Fast Startup" to accelerate the boot process. This feature, enabled by default, utilizes a hybrid approach, combining elements of both hibernation and a cold boot. When the system shuts down, it saves the kernel and device drivers to a special hibernation file on the hard drive. Upon restart, the system loads this file, significantly reducing the time required for booting. The implementation of Fast Startup effectively renders the traditional hibernate function redundant, as it achieves a similar outcome with enhanced speed and efficiency.
2. SSD Prevalence: The widespread adoption of Solid State Drives (SSDs) has drastically reduced the time it takes to boot a computer. SSDs, with their significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), eliminate the need for hibernation as a method to speed up boot times. The benefits of hibernation, in terms of boot speed, are largely negated by the inherent performance advantage of SSDs.
3. Power Management Improvements: Windows 11 incorporates sophisticated power management features that dynamically adjust power consumption based on user activity and system load. These features, coupled with the efficiency of modern hardware, effectively minimize the need for hibernation as a power-saving mechanism.
4. System Stability: In certain cases, the absence of hibernate might be linked to system stability issues. While not a common occurrence, potential conflicts between hibernation functionality and specific hardware configurations or software applications could necessitate its disablement.
5. User Preferences: Windows 11 allows users to customize power options, including the ability to disable hibernate. This option might be chosen by users who prioritize other power management settings or who simply prefer not to utilize the hibernate feature.
The Benefits of the Change
While the absence of hibernate might initially seem like a limitation, it often reflects a deliberate design choice aimed at optimizing user experience and system performance. The following benefits highlight the advantages of this change:
- Enhanced Boot Speed: Fast Startup, as discussed earlier, significantly accelerates the boot process, achieving a similar outcome as hibernation without the need for a separate feature.
- Improved Power Efficiency: Windows 11’s advanced power management features, combined with the efficiency of modern hardware, effectively minimize the need for hibernation as a power-saving mechanism.
- Reduced System Complexity: Eliminating the hibernation feature simplifies the system’s power management options, leading to a cleaner and more intuitive user interface.
- Potential for Stability Improvements: Disabling hibernate in specific scenarios can contribute to overall system stability by eliminating potential conflicts with hardware or software.
FAQs on Hibernate in Windows 11
1. Why is hibernate disabled on my Windows 11 computer?
The disablement of hibernate in Windows 11 is often attributed to the implementation of Fast Startup, the prevalence of SSDs, and the advanced power management features incorporated into the operating system.
2. Can I re-enable hibernate in Windows 11?
While the hibernate option might not be readily available, it can be re-enabled through the Command Prompt or by modifying the registry. However, it’s important to note that re-enabling hibernate might affect the efficiency of Fast Startup and potentially introduce compatibility issues.
3. Are there any downsides to disabling hibernate?
Disabling hibernate does not significantly impact the functionality of Windows 11. The benefits of Fast Startup and the efficiency of modern hardware effectively negate the need for hibernation.
4. What is the difference between hibernate and sleep mode?
Hibernate saves the current state of the operating system and all open applications to the hard drive, allowing for a faster boot-up time than a cold start. Sleep mode, on the other hand, keeps the computer in a low-power state while retaining data in RAM, resulting in a faster resume time but requiring continuous power supply.
5. How can I find out if hibernate is disabled on my Windows 11 computer?
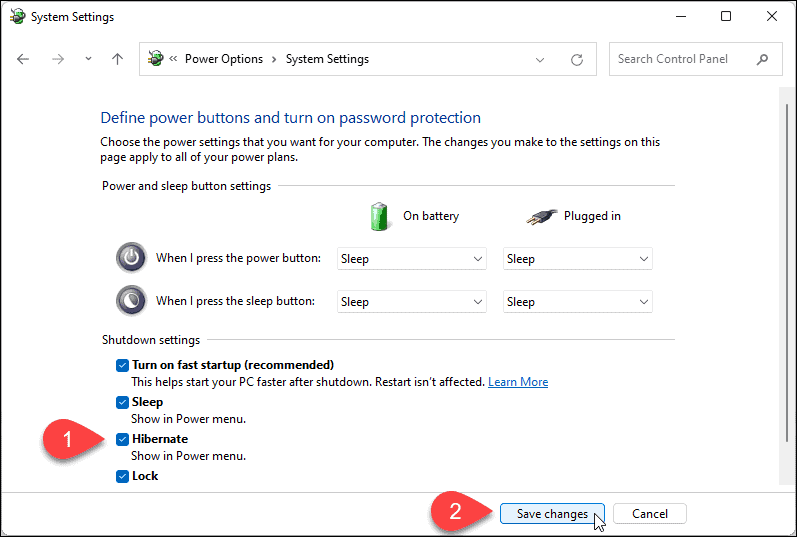
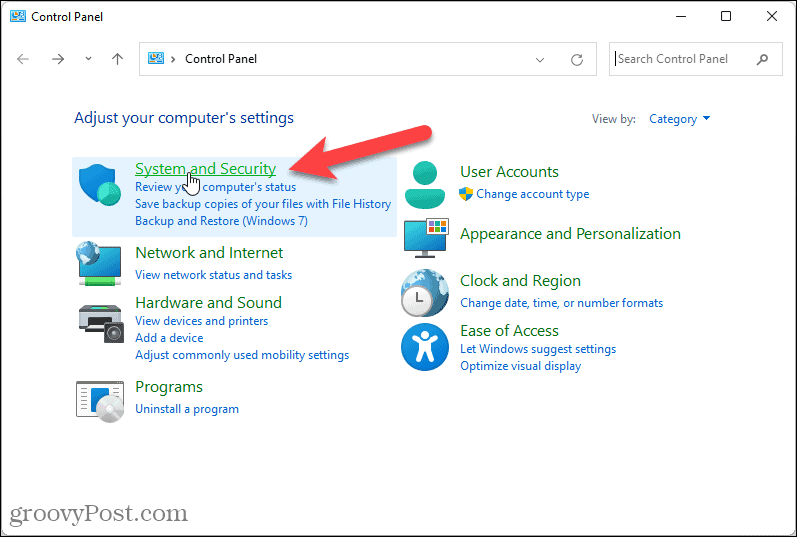
You can check if hibernate is disabled by opening the Power Options settings in the Control Panel. If the "Hibernate" option is not listed, it is likely disabled.
Tips for Optimizing Power Management in Windows 11
- Utilize Power Options: The Power Options settings in the Control Panel allow you to customize power management settings, including the ability to adjust screen brightness, sleep mode settings, and other power-saving features.
- Manage Power Plan: Windows 11 offers various power plans, each tailored to specific usage scenarios. Choose the power plan that best suits your needs, whether you prioritize performance, battery life, or a balance between the two.
- Optimize System Settings: Explore system settings to adjust power-related options, such as the timeout for turning off the display or putting the computer to sleep.
- Install Latest Updates: Windows 11 updates often include enhancements to power management features. Ensure that your system is up-to-date to benefit from the latest improvements.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If you’re concerned about power efficiency, consider upgrading your hardware, particularly the CPU and storage drive. Modern components are designed to be more power-efficient, contributing to longer battery life and reduced energy consumption.
Conclusion
The absence of hibernate in Windows 11 is not a bug or a limitation but rather a reflection of the operating system’s focus on efficiency and modern user experience. Fast Startup, the prevalence of SSDs, and advanced power management features effectively address the benefits traditionally associated with hibernate. While the option might not be readily available, understanding the reasons behind its absence and the benefits it brings can enhance your understanding of Windows 11 and its commitment to providing a seamless and optimized computing experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery: Why is Hibernate Disabled in Windows 11?. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
