Unveiling the Enigma: Why Windows 11 Might Fail to Load Correctly
Related Articles: Unveiling the Enigma: Why Windows 11 Might Fail to Load Correctly
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Enigma: Why Windows 11 Might Fail to Load Correctly. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Enigma: Why Windows 11 Might Fail to Load Correctly

The ubiquitous blue screen of death, or the less dramatic but equally frustrating "Windows failed to start" message, can be a disheartening sight for any Windows 11 user. While the underlying causes can be complex and multifaceted, understanding the common culprits and troubleshooting techniques can empower users to regain control and restore their system’s functionality. This article delves into the intricacies of Windows 11 loading issues, offering a comprehensive exploration of potential causes, effective solutions, and preventative measures.
Understanding the "Windows Failed to Load Correctly" Error
This error message, often accompanied by a specific error code, signals that the operating system encountered a critical failure during the boot process. The failure could stem from various factors, including:
- Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty RAM, a failing hard drive, or an incompatible component can disrupt the boot sequence.
- Software Conflicts: Outdated or corrupted drivers, incompatible applications, or malicious software can interfere with the system’s core functions.
- Operating System Errors: Corrupted system files, incorrect registry entries, or incomplete updates can hinder the operating system’s ability to load.
- Boot Configuration Issues: Improperly configured boot settings, such as incorrect boot order or missing boot files, can prevent the system from accessing the necessary files.
- External Factors: Power surges, sudden shutdowns, or external hardware connections can lead to data corruption or system instability.
Delving into the Causes: A Closer Look
1. Hardware Malfunctions:
- RAM Errors: Faulty RAM modules can cause random system crashes, including boot failures. Performing a memory test using the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool or a dedicated memory testing utility can help identify problematic RAM modules.
- Hard Drive Issues: A failing hard drive can manifest as slow performance, data loss, and boot failures. Checking for bad sectors using the CHKDSK command or a disk health monitoring tool can reveal potential problems.
- Other Hardware: Other components, such as the motherboard, power supply, or graphics card, can also contribute to boot failures. Diagnosing these issues requires a more specialized approach, potentially involving hardware testing or replacement.
2. Software Conflicts:
- Driver Issues: Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause conflicts with the operating system, leading to boot failures. Updating drivers through the Device Manager or the manufacturer’s website can resolve these issues.
- Incompatible Applications: Certain applications, especially those with outdated or incompatible components, can interfere with the boot process. Removing recently installed applications or disabling conflicting programs can help.
- Malware Infections: Malware can corrupt system files, modify boot settings, or introduce malicious code, leading to boot failures. Running a comprehensive antivirus scan can help detect and remove malware.
3. Operating System Errors:
- Corrupted System Files: System files can become corrupted due to software failures, hardware errors, or improper updates. Running the System File Checker (SFC) tool can help repair damaged system files.
- Registry Issues: The Windows Registry, a database containing system settings, can become corrupted, leading to boot failures. Using a registry cleaner tool or manually checking for errors can help resolve these issues.
- Incomplete Updates: Incomplete or failed Windows updates can cause system instability and boot failures. Ensuring that all updates are successfully installed can prevent these problems.
4. Boot Configuration Issues:
- Incorrect Boot Order: The boot order, which determines the sequence in which the system tries to boot from different devices, must be configured correctly. Changing the boot order in the BIOS settings can resolve issues related to booting from the wrong device.
- Missing Boot Files: Essential boot files, such as the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), can become corrupted or missing, preventing the system from booting. Using the Bootrec command-line tool can help repair or rebuild the BCD.
5. External Factors:
- Power Surges: Power surges can damage hardware components or corrupt data, leading to boot failures. Using a surge protector can help mitigate the risks associated with power fluctuations.
- Sudden Shutdowns: Abruptly shutting down the system without proper shutdown procedures can cause data corruption and boot failures. Ensuring a clean shutdown can prevent these issues.
- External Hardware Connections: Connecting external devices, especially those with incompatible drivers, can sometimes cause boot failures. Removing unnecessary external devices can help resolve these problems.
Troubleshooting: A Step-by-Step Approach
1. Basic Troubleshooting:
- Restart the System: A simple restart can sometimes resolve temporary issues that might be preventing the system from booting correctly.
- Check for Loose Connections: Ensure that all cables and connections are securely plugged in.
- Remove External Devices: Disconnect any external devices that are not essential for booting.
- Try Booting in Safe Mode: Booting in Safe Mode, a diagnostic mode that loads only essential drivers and services, can help identify conflicts or issues that might be preventing the system from booting normally.
2. System File Checker (SFC):
- Open Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Start menu, right-click on the Command Prompt icon, and select "Run as administrator."
- Run SFC Scan: Type "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt window and press Enter. This will scan system files for corruption and attempt to repair any errors found.
3. Bootrec Command-line Tool:
- Open Command Prompt: Follow the steps outlined above to open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Run Bootrec Commands: The Bootrec tool can be used to repair boot files, rebuild the BCD, and fix boot sector issues. Refer to Microsoft’s documentation for detailed commands and instructions.
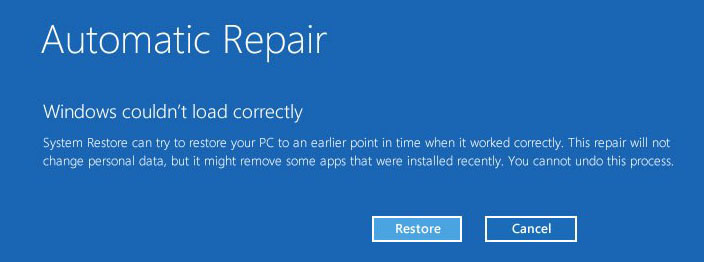
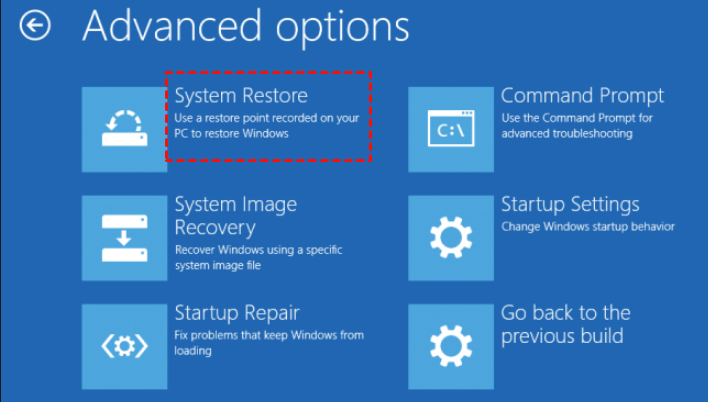
4. System Restore:
- Access System Restore: Open the Start menu, search for "System Restore," and select the option.
- Choose a Restore Point: Select a restore point created before the boot issues started. System Restore will revert the system to a previous state, potentially resolving the problem.
5. Reinstall Windows:
- Create a Bootable USB Drive: Download the Windows 11 installation media from Microsoft’s website and create a bootable USB drive.
- Boot from USB: Change the boot order in the BIOS settings to boot from the USB drive.
- Install Windows: Follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows 11. This will erase all data on the system drive, so ensure that important files are backed up beforehand.
6. Contact Support:
If the above troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the issue, it’s recommended to contact Microsoft support or a qualified computer technician for further assistance.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the error code displayed alongside the "Windows failed to load correctly" message?
A: The error code provides a specific indication of the underlying cause of the boot failure. Referencing Microsoft’s documentation or online resources can help interpret the code and identify potential solutions.
Q: What steps should I take if my system repeatedly fails to boot after attempting troubleshooting steps?
A: If the problem persists, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance from a computer technician or Microsoft support. They can perform more in-depth diagnostics and potentially identify hardware failures or complex software issues.
Q: Can I prevent these boot failures from occurring in the future?
A: While it’s impossible to completely eliminate the possibility of boot failures, proactive measures can significantly reduce their occurrence. These include:
- Regularly Updating Drivers: Keeping drivers up-to-date ensures compatibility with the operating system and reduces the risk of conflicts.
- Performing Regular System Maintenance: Running disk cleanup tools, defragmenting the hard drive, and scanning for malware can help maintain system stability.
- Creating System Restore Points: Regularly creating system restore points allows you to revert to a previous state if boot failures occur.
- Using a Surge Protector: Protecting your system from power surges can prevent hardware damage and data corruption.
- Shutting Down Properly: Always shut down the system gracefully to avoid data corruption and potential boot issues.
Conclusion:
Encountering a "Windows failed to load correctly" error can be a frustrating experience, but understanding the potential causes and troubleshooting techniques empowers users to regain control of their systems. By systematically investigating the problem, utilizing available tools, and taking preventative measures, users can mitigate the risk of future boot failures and ensure a smooth and reliable Windows 11 experience. Remember, seeking professional assistance when necessary can provide a more comprehensive and efficient solution.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Enigma: Why Windows 11 Might Fail to Load Correctly. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
