windows 11 size vs 10
Related Articles: windows 11 size vs 10
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to windows 11 size vs 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 11 vs. Windows 10: A Comparative Analysis of System Requirements and Performance

The transition from Windows 10 to Windows 11 has sparked numerous discussions, with one key area of concern being the shift in system requirements. While both operating systems offer a multitude of features and functionalities, Windows 11’s introduction of new hardware specifications has prompted users to consider whether their existing systems are compatible and if the upgrade is worthwhile. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of the system requirements for Windows 11 and Windows 10, exploring the implications of these differences on performance, compatibility, and user experience.
Understanding the System Requirements
System requirements define the minimum hardware specifications necessary for an operating system to function optimally. These requirements include factors like processor, RAM, storage space, and graphics capabilities. Windows 11, in comparison to Windows 10, has introduced stricter requirements, aiming to optimize performance for newer hardware and support advanced features.
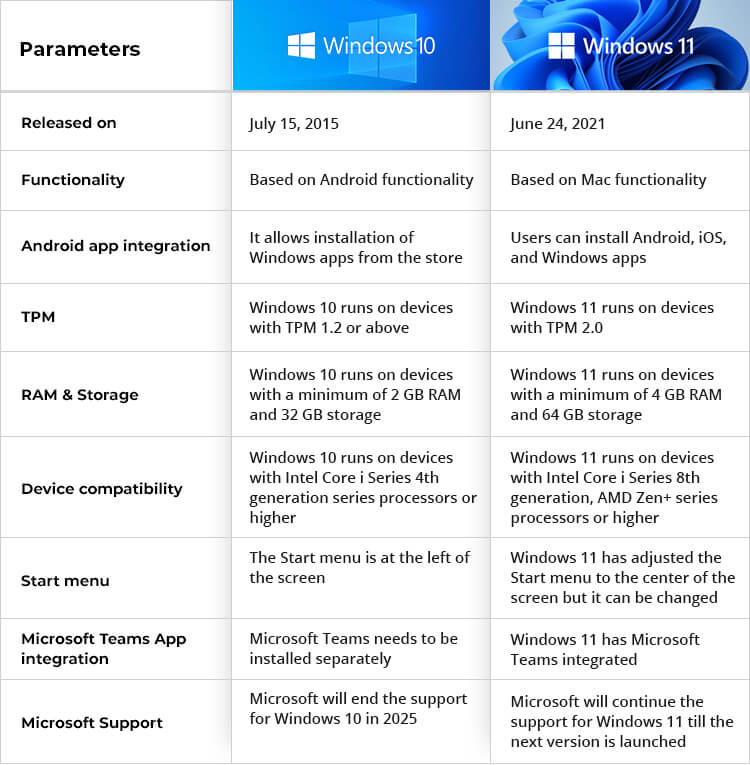
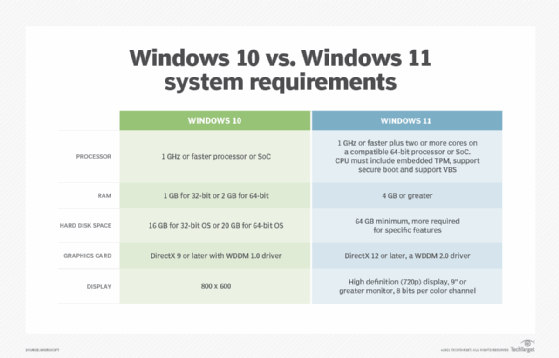
Processor Requirements:
- Windows 10: Supports a broad range of processors, including older models, as long as they meet the minimum requirements for the specific edition.
- Windows 11: Requires a 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster processor with two or more cores, compatible with 64-bit architecture. This emphasis on newer processors signifies a focus on improved performance and compatibility with the latest hardware technologies.
RAM Requirements:
- Windows 10: Minimum requirement is 1 GB for 32-bit and 2 GB for 64-bit versions, with higher recommendations for smoother multi-tasking.
- Windows 11: Requires a minimum of 4 GB RAM, reflecting the increased demands of modern applications and features. This higher requirement ensures smoother operation and prevents system slowdowns, particularly when running resource-intensive programs.
Storage Space:
- Windows 10: Minimum requirement is 16 GB for 32-bit and 20 GB for 64-bit versions, with larger storage options recommended for storing applications and data.
- Windows 11: Requires a minimum of 64 GB storage space, reflecting the larger size of the operating system and the need for adequate space for system files, applications, and user data.
Graphics Card Requirements:
- Windows 10: No specific graphics card requirements, although a compatible graphics driver is necessary for optimal performance.
- Windows 11: Requires a compatible graphics card that supports DirectX 12 or later, indicating a focus on improved visual fidelity and enhanced gaming capabilities.
TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot:
- Windows 10: These features are not mandatory for installation.
- Windows 11: Requires a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip and Secure Boot enabled in the BIOS settings. These security features enhance system security and protect against potential threats.
Implications of System Requirements
The stricter system requirements of Windows 11 can have several implications for users:
- Hardware Compatibility: Older systems that do not meet the minimum requirements may not be able to upgrade to Windows 11. This can lead to users needing to replace their hardware or continue using Windows 10.
- Performance Enhancement: The focus on newer hardware in Windows 11 aims to improve performance, particularly in areas like multitasking, application responsiveness, and gaming.
- Security Enhancements: The requirement for TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot enhances system security, making it more resistant to malware and other threats.
- User Experience: Windows 11 introduces a redesigned user interface and new features, which may be more appealing to users with newer hardware.
Benefits of Upgrading to Windows 11:
While the stricter system requirements may present challenges for some users, upgrading to Windows 11 offers several potential benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: The focus on newer hardware can lead to improved performance, faster application loading times, and smoother multitasking.
- Modern User Interface: Windows 11 features a redesigned user interface, offering a more intuitive and visually appealing experience.
- New Features: Windows 11 introduces new features such as Android app support, a redesigned Start menu, and improved multitasking capabilities.
- Security Improvements: The requirement for TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot enhances system security, making it more resistant to threats.
Considerations for Upgrading
Before upgrading to Windows 11, users should carefully consider the following factors:
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure that their system meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11.
- Data Backup: Create a backup of important data before upgrading to prevent data loss.
- Application Compatibility: Check if all essential applications are compatible with Windows 11.
- Performance Impact: Consider the potential impact of the upgrade on system performance, particularly for older systems.
FAQs about Windows 11 vs. Windows 10 System Requirements:
Q: Can I still use Windows 10 after upgrading to Windows 11?
A: No, you cannot revert to Windows 10 after upgrading to Windows 11 without a clean installation.
Q: What happens if my system does not meet the Windows 11 requirements?
A: You will not be able to upgrade to Windows 11. You can either continue using Windows 10 or upgrade your hardware to meet the requirements.
Q: Is it worth upgrading to Windows 11 if my system meets the requirements?
A: This depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider the benefits of Windows 11, such as enhanced performance and new features, and weigh them against potential drawbacks, such as application compatibility issues.
Q: Can I install Windows 11 on a virtual machine?
A: Yes, you can install Windows 11 on a virtual machine, even if your physical system does not meet the minimum requirements. However, performance may be impacted.
Tips for Upgrading to Windows 11:
- Check System Requirements: Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements before attempting to upgrade.
- Back Up Data: Create a backup of important data to prevent data loss during the upgrade process.
- Check Application Compatibility: Verify that essential applications are compatible with Windows 11.
- Perform a Clean Installation: Consider performing a clean installation of Windows 11 for optimal performance and to remove any potential conflicts from previous operating systems.
- Use the Windows 11 Installation Assistant: Use the official Windows 11 Installation Assistant to guide you through the upgrade process.
Conclusion:
The shift in system requirements between Windows 10 and Windows 11 reflects the evolution of technology and the increasing demands of modern operating systems. While the stricter requirements may pose challenges for some users, they also pave the way for enhanced performance, security, and a modern user experience. Before upgrading, users should carefully assess their system’s compatibility, consider the potential benefits and drawbacks, and take necessary precautions to ensure a smooth transition. Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to Windows 11 depends on individual needs and priorities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 11 size vs 10. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
