windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage
Related Articles: windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 11 vs. Windows 10: A Comparative Analysis of RAM Usage

The evolution of operating systems is a constant pursuit of efficiency and performance. Microsoft’s Windows 11, the latest iteration of its flagship operating system, arrived with a suite of new features and improvements, including a redesigned user interface and enhanced security measures. However, one of the key areas that frequently sparks debate is RAM usage. This article delves into a comparative analysis of Windows 11 and Windows 10 RAM consumption, examining the factors influencing RAM utilization and the implications for user experience.
Understanding RAM Consumption
RAM, or Random Access Memory, serves as the primary workspace for an operating system and its applications. It acts as a temporary storage location for data that the system is actively using, ensuring quick access and seamless operation. When an operating system or application requires more data than available RAM, it turns to secondary storage, such as the hard drive or SSD, which is significantly slower. This process, known as "paging," can lead to noticeable performance degradation.
Factors Influencing RAM Usage
Several factors contribute to the RAM consumption of an operating system, including:
- System Architecture: The underlying architecture of the operating system, including the kernel and core services, directly impacts its RAM footprint.
- Installed Applications: The number and types of applications installed on a system significantly influence RAM usage. Resource-intensive applications, such as gaming software or video editing tools, require more RAM to operate smoothly.
- Background Processes: Numerous background processes run concurrently, including system services, updates, and user-installed software. These processes consume RAM even when not actively in use.
- User Habits: The number of open applications, browser tabs, and other active processes directly impact RAM consumption.
Windows 11 vs. Windows 10: A Comparative Perspective
While both Windows 11 and Windows 10 are capable operating systems, there are notable differences in their RAM utilization patterns.
- Windows 11’s Increased RAM Consumption: Initial reports and user feedback indicated that Windows 11 exhibited higher RAM consumption compared to Windows 10. This was attributed to several factors, including the introduction of new features, such as the "Start" menu redesign and the "Windows Sandbox" feature, which require additional RAM resources.
- Optimization Efforts: Microsoft has acknowledged the concerns regarding RAM usage and implemented several optimizations in subsequent Windows 11 updates. These updates have aimed to reduce background processes, refine resource allocation, and enhance overall efficiency.
- System Configuration: The actual RAM usage in Windows 11 can vary significantly depending on the system configuration, including the amount of RAM installed, the processor type, and the installed applications.
Impact of RAM Usage on Performance
Higher RAM consumption can potentially impact system performance, leading to:
- Slower Application Launch Times: Applications may take longer to load and respond to user input if insufficient RAM is available.
- Increased Latency: The system might experience noticeable delays in processing tasks, particularly when multitasking or running resource-intensive applications.
- System Slowdown: In extreme cases, excessive RAM usage can lead to system slowdown, where the operating system becomes unresponsive and sluggish.
Tips for Managing RAM Usage
- Optimize System Settings: Configure Windows settings to reduce unnecessary background processes, disable unused features, and optimize power settings.
- Close Unused Applications: Regularly close applications that are not actively being used to free up RAM resources.
- Limit Browser Tabs: Excessive browser tabs consume significant RAM. Consider closing unused tabs or using tab management extensions.
- Monitor RAM Usage: Utilize system monitoring tools to track RAM consumption and identify processes that are consuming excessive resources.
- Upgrade RAM: If you consistently experience RAM-related performance issues, consider upgrading to a system with more RAM.
FAQs
Q: Does Windows 11 require more RAM than Windows 10?
A: While Windows 11 initially showed higher RAM consumption, Microsoft has implemented optimizations to improve efficiency. The actual RAM requirements depend on the system configuration and usage patterns.
Q: How much RAM do I need for Windows 11?
A: Microsoft recommends a minimum of 4GB of RAM for Windows 11, but for optimal performance, 8GB or more is recommended.
Q: How can I check my RAM usage in Windows 11?
A: You can check your RAM usage using the Task Manager (press Ctrl+Shift+Esc). The "Performance" tab displays detailed information about RAM usage.
Q: Is it possible to reduce RAM usage in Windows 11?
A: Yes, there are several ways to reduce RAM usage in Windows 11, including optimizing system settings, closing unused applications, and limiting browser tabs.
Conclusion
Windows 11 and Windows 10 represent advancements in operating system technology, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. While Windows 11 initially demonstrated higher RAM consumption, Microsoft’s ongoing optimization efforts have addressed these concerns. The actual RAM usage depends on various factors, including system configuration, installed applications, and user habits. By understanding the factors influencing RAM usage and implementing best practices for RAM management, users can ensure optimal performance and a seamless experience on both Windows 11 and Windows 10.

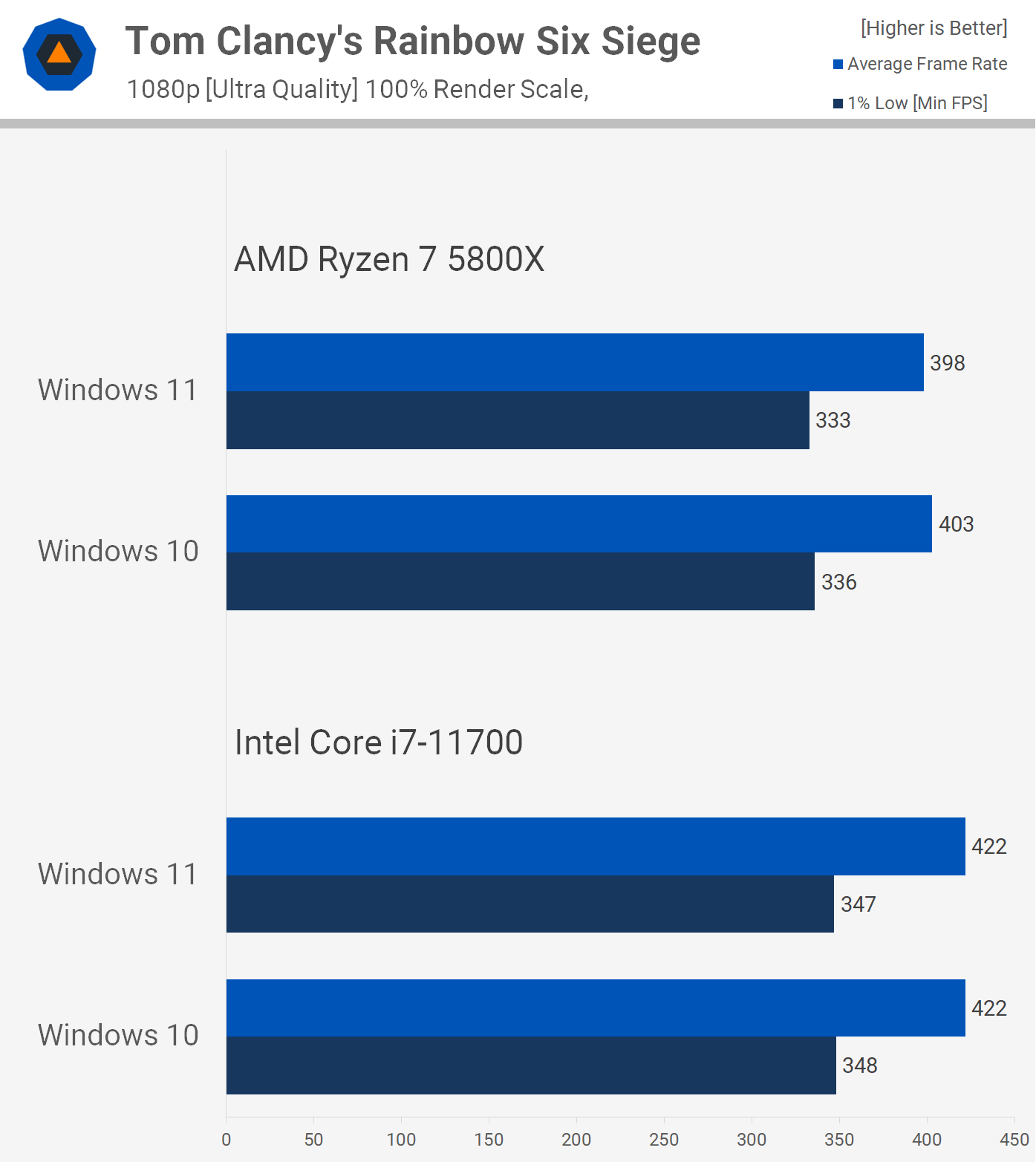

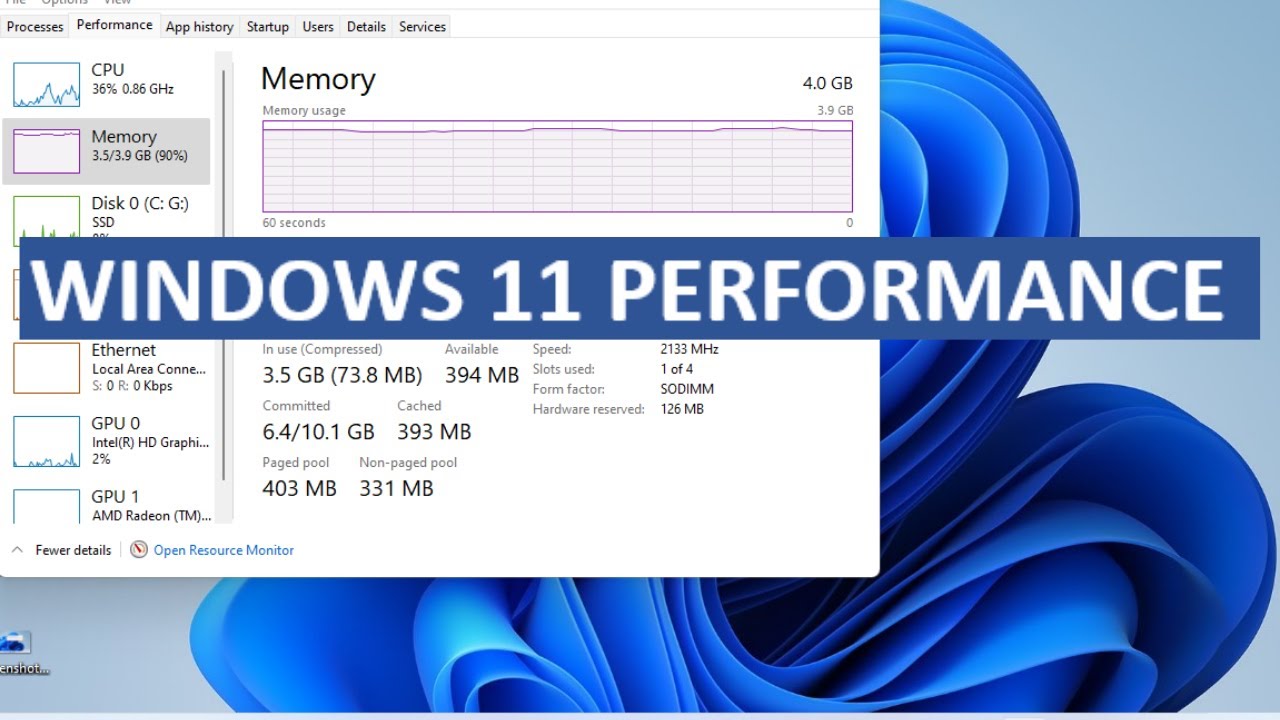
![[OLD] Not Relevant!!! windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage использование ОЗУ Gaming Performance](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_IjkVw6in4Y/maxresdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 11 vs windows 10 ram usage. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
