windows 11 without tpm 2.0 download
Related Articles: windows 11 without tpm 2.0 download
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to windows 11 without tpm 2.0 download. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11: A Guide to Installing Without TPM 2.0

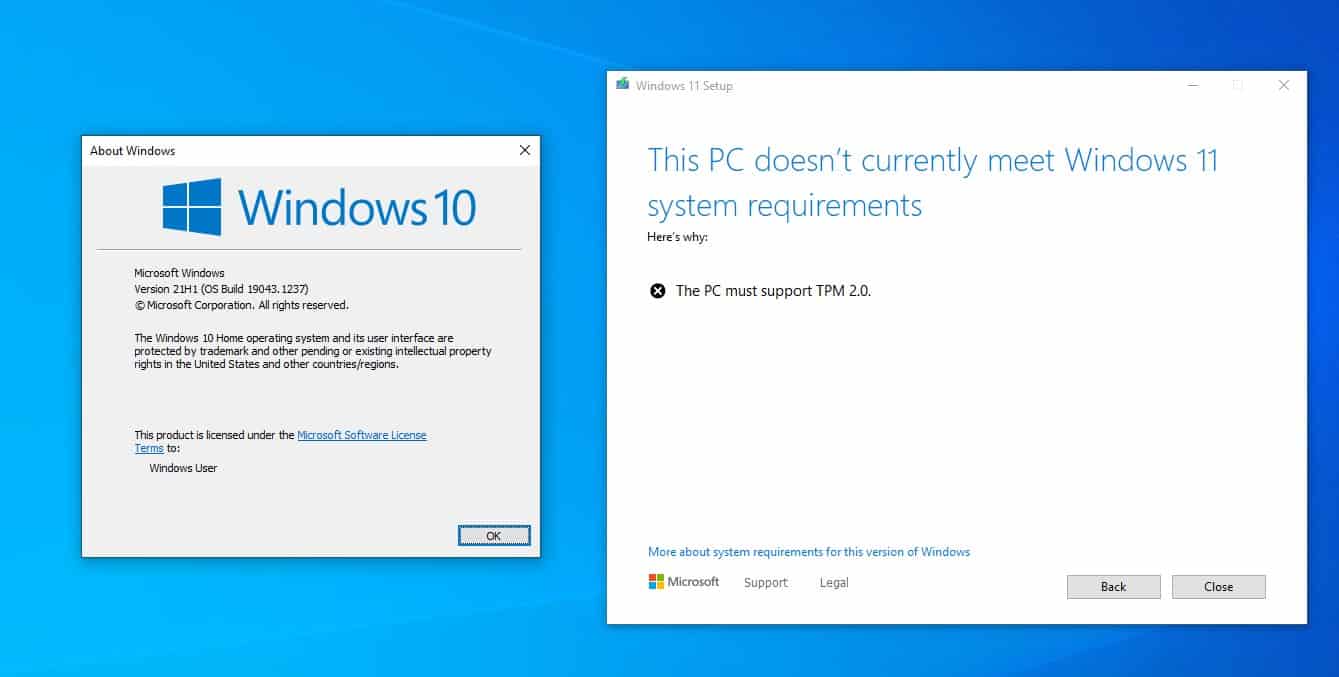
The release of Windows 11 brought with it a new set of requirements for users to upgrade or install the operating system. One of the most prominent and debated requirements was the presence of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip on the user’s computer. This requirement, aimed at enhancing security and data protection, presented a challenge for many users with older hardware lacking the necessary TPM chip.
This article delves into the complexities of installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip, exploring the reasons behind the requirement, the potential risks involved, and the alternative pathways available to users.
Understanding the Importance of TPM 2.0
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated hardware component embedded within the motherboard of a computer. It acts as a secure cryptographic processor, generating and storing encryption keys, protecting user data from unauthorized access and tampering. TPM 2.0, the latest version of this technology, offers enhanced security features compared to its predecessor, TPM 1.2.
Windows 11 leverages the capabilities of TPM 2.0 to bolster security measures. It uses the chip to:
- Securely store encryption keys: These keys are crucial for encrypting data on the hard drive, protecting it from unauthorized access even if the operating system is compromised.
- Verify the integrity of the operating system: TPM 2.0 helps ensure that the operating system has not been tampered with, preventing malicious software from altering critical system files.
- Enable secure boot: This feature ensures that only trusted operating systems and drivers can be loaded, preventing the execution of malware before the operating system starts.
- Enhance authentication processes: TPM 2.0 supports secure authentication methods, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access the system.
The Challenges of Installing Without TPM 2.0
While the security benefits of TPM 2.0 are undeniable, the requirement for it presents a significant challenge for users with older hardware that lacks the chip. Installing Windows 11 on such systems without a TPM 2.0 chip can be accomplished, but it comes with potential risks and drawbacks:
- Compromised Security: Bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement weakens the security measures implemented by Windows 11, leaving the system vulnerable to various security threats.
- Potential for Malware: Without the protection of TPM 2.0, the system becomes more susceptible to malware infections, as malicious software can more easily gain access and control.
- Limited Compatibility: Some features and functionalities of Windows 11 may not work optimally or at all without a TPM 2.0 chip, leading to a less seamless user experience.
- Future Updates: Microsoft may discontinue support for systems without TPM 2.0 in future Windows 11 updates, making it impossible to receive security patches and other important updates.
Exploring Alternative Pathways
Despite the challenges, several options exist for users who want to install Windows 11 on systems without a TPM 2.0 chip.
- Enabling Emulated TPM: Some motherboards, even if they lack a dedicated TPM 2.0 chip, may offer the ability to emulate its functionality using firmware settings in the BIOS. This can be achieved by enabling the "fTPM" option in the BIOS settings, creating a virtual TPM environment that allows Windows 11 to recognize it as a valid TPM 2.0 chip.
- Using a USB TPM: External TPM 2.0 modules are available in the form of USB devices. These modules connect to the computer via a USB port and provide the necessary security functions required by Windows 11. However, it is important to note that the performance of the system may be affected due to the additional hardware and software interaction.
- Using a Registry Tweak: This method involves modifying the Windows registry to bypass the TPM 2.0 check during installation. However, this is a risky approach as it can potentially lead to system instability and security vulnerabilities. It is strongly advised to explore other options before resorting to this method.
- Installing Windows 11 without TPM 2.0 (Unsupported): This method involves using a modified installation media that bypasses the TPM 2.0 check, allowing installation on unsupported hardware. However, this is highly discouraged as it compromises system security and may lead to compatibility issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it safe to install Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: Installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip significantly compromises the security of the system, making it more vulnerable to malware and other threats. It is not recommended to install Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip unless absolutely necessary.
Q: What are the consequences of installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: You may experience security vulnerabilities, limited compatibility with certain features, and potential issues with future updates.
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 from Windows 10 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: While it might be possible to bypass the TPM 2.0 requirement during the upgrade process, it is not recommended. You may face similar security risks and compatibility issues as with a fresh installation.
Q: Can I use a virtual machine to install Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: Yes, you can install Windows 11 within a virtual machine, which can be configured to emulate a TPM 2.0 chip. However, this approach may result in performance limitations.
Tips for Installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 Chip
- Consider the risks: Carefully evaluate the potential security risks and compatibility issues associated with installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip.
- Explore alternatives: Investigate alternative options like enabling an emulated TPM or using a USB TPM module before attempting to bypass the requirement.
- Seek professional guidance: If you are unsure about the process or concerned about the risks, consult with a qualified IT professional for assistance.
- Keep your system updated: Regularly update your system with the latest security patches and software updates to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Installing Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip presents a significant security risk and compromises the integrity of the operating system. While alternative methods exist to bypass the requirement, they should be approached with caution and only considered as a last resort. For optimal security and performance, it is highly recommended to ensure your system meets the minimum requirements, including the presence of a TPM 2.0 chip, before installing or upgrading to Windows 11.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 11 without tpm 2.0 download. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
