windows 11 without tpm 2.0
Related Articles: windows 11 without tpm 2.0
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to windows 11 without tpm 2.0. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Without TPM 2.0: A Comprehensive Guide

Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system, with its modern design and enhanced features, has garnered significant attention. However, its stringent hardware requirements, particularly the demand for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 chip, have presented a challenge for some users. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Windows 11 without TPM 2.0, exploring its implications, potential workarounds, and the evolving landscape of security and compatibility.
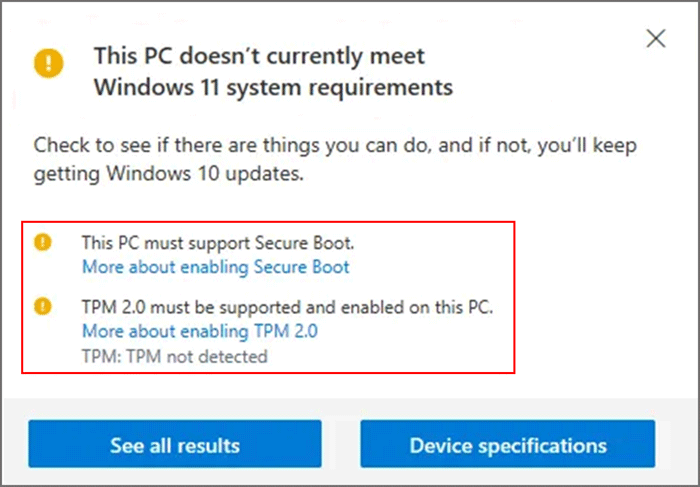
Understanding the Importance of TPM 2.0
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated microchip embedded on a computer’s motherboard. It acts as a hardware-based security component, safeguarding sensitive data and system integrity. TPM 2.0, the latest version, enhances security by employing advanced cryptographic techniques and supporting features like secure boot and disk encryption.
In the context of Windows 11, the requirement for TPM 2.0 stems from Microsoft’s commitment to elevating security standards. This chip plays a crucial role in:
- Secure Boot: Preventing unauthorized software from loading during system startup, thereby mitigating the risk of malware infections.
- Disk Encryption: Ensuring that data stored on the device remains encrypted, even if the device is stolen or compromised.
- Password Protection: Securing passwords and other sensitive credentials, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access them.
- Platform Integrity: Verifying the authenticity and integrity of the operating system and other critical components, minimizing the possibility of tampering or malicious modifications.
Navigating the Compatibility Gap: Windows 11 Without TPM 2.0
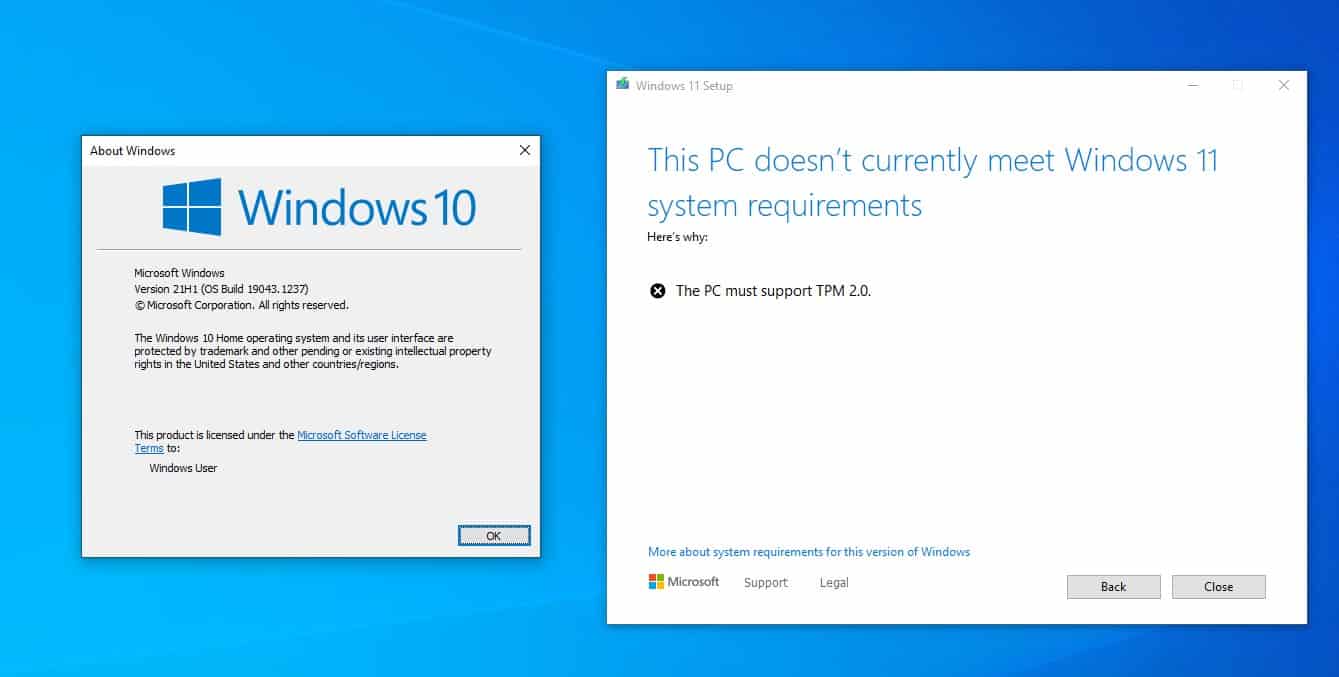
While TPM 2.0 is a vital security enhancement, not all computers meet this requirement. Older systems, especially those manufactured before 2016, may lack this chip. This poses a challenge for users who wish to upgrade to Windows 11, leading them to explore alternative paths.
Workarounds and Alternatives
While Microsoft strongly recommends TPM 2.0 for optimal security and compatibility, there are workarounds and alternatives for users who find themselves in this situation:
- Enabling TPM 2.0 in the BIOS: Some motherboards may have TPM 2.0 capabilities that are disabled by default. Accessing the BIOS settings and enabling TPM 2.0 could resolve the issue.
- Virtualization Solutions: Utilizing virtual machines (VMs) such as VMware or VirtualBox allows users to install and run Windows 11 on a virtualized environment, potentially bypassing the TPM requirement. However, performance might be affected, and it’s important to note that security implications might arise in a virtualized environment.
- Registry Modification: This method involves manually modifying registry settings to bypass the TPM 2.0 check. However, this approach is not recommended as it can lead to system instability and potential security vulnerabilities.
- Using Windows 11 Insider Preview Builds: Microsoft offers Insider Preview builds of Windows 11, which may allow users to install the operating system without a TPM 2.0 chip. However, these builds are in development and may contain bugs or instability.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
While these workarounds offer temporary solutions, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential risks associated with running Windows 11 without TPM 2.0:
- Compromised Security: The absence of TPM 2.0 weakens the system’s defenses, making it more susceptible to malware attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications and features might not function correctly or might be unavailable without TPM 2.0.
- Future Updates: Microsoft may discontinue support for older systems without TPM 2.0, limiting access to security updates and new features.
The Future of Windows 11 and TPM 2.0
The evolution of Windows 11 and its security requirements is a continuous process. Microsoft is committed to enhancing security and ensuring that its operating systems are equipped with robust safeguards. As technology advances, the importance of TPM 2.0 is likely to grow.
FAQs: Windows 11 Without TPM 2.0
Q: Is it possible to install Windows 11 without TPM 2.0?
A: While Microsoft recommends TPM 2.0 for optimal security and compatibility, it is possible to install Windows 11 without it using workarounds. However, this is not recommended due to potential security risks and compatibility issues.
Q: What are the risks of using Windows 11 without TPM 2.0?
A: Running Windows 11 without TPM 2.0 compromises security, making the system more susceptible to malware attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Additionally, it can lead to compatibility issues with certain applications and features.
Q: Is there a way to upgrade my older computer to meet the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: Some motherboards may have TPM 2.0 capabilities that are disabled by default. Accessing the BIOS settings and enabling TPM 2.0 could resolve the issue. However, if your motherboard does not support TPM 2.0, you might need to consider purchasing a new computer.
Q: Will Microsoft continue to support older systems without TPM 2.0?
A: Microsoft may discontinue support for older systems without TPM 2.0 in the future, limiting access to security updates and new features.
Tips for Using Windows 11 Without TPM 2.0
- Exercise Extreme Caution: When using Windows 11 without TPM 2.0, exercise extreme caution by avoiding suspicious websites, downloading files from untrusted sources, and keeping your software updated.
- Utilize Strong Passwords: Employ strong and unique passwords for all accounts, and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Consider Antivirus Software: Install and regularly update reputable antivirus software to protect your system from malware.
- Backup Your Data: Regularly back up your important data to an external drive or cloud storage service to mitigate the impact of data loss.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Security and Compatibility
The requirement for TPM 2.0 in Windows 11 reflects Microsoft’s commitment to enhancing security and safeguarding user data. While this requirement presents challenges for users with older systems, understanding the risks and benefits associated with running Windows 11 without TPM 2.0 is crucial.
While workarounds exist, they should be approached with caution, acknowledging the potential security implications. Ultimately, a balanced approach that prioritizes both security and compatibility is essential for a positive user experience. As technology evolves, it’s likely that TPM 2.0 will become increasingly prevalent, shaping the future of computing security.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into windows 11 without tpm 2.0. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
